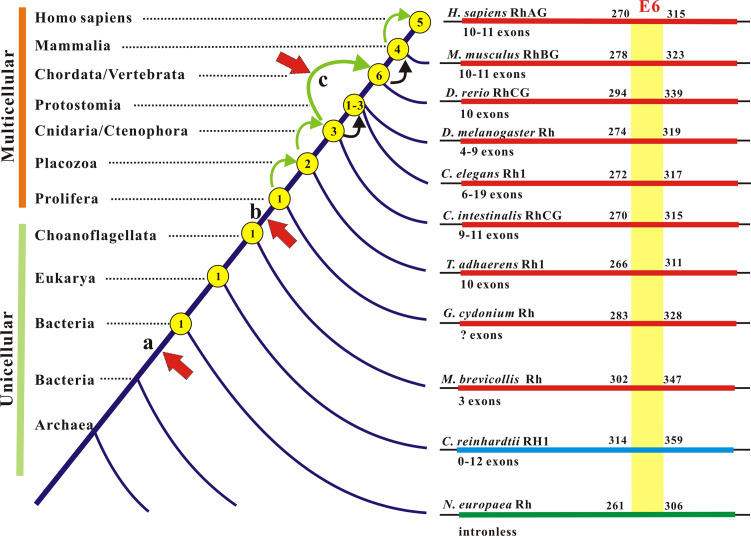
Fig. 2.
Gene gain and gene loss in the genesis and evolution of the Rh protein family. Left Gene gain and loss are denoted by copy numbers (circled) on the tree trunk (not to scale). Bending arrows indicate gene duplications (green) or gene contractions (black). The increase from three to six genes may arise by a genome-wide duplication. Vertical arrows to the truck point to evolutionary events with which Rh gene duplications coincide: a origin of an ancient Rh gene and its branch off Amt genes in Bacteria and Archaea below the arrow; b origin of epithelia; c origin of erythrocyte. Right Exon remodeling in Rh family genes from representative taxa is shown. E6 (exon 6), the most conserved exon encoding 46 amino acids in metazoans, is used as a reference