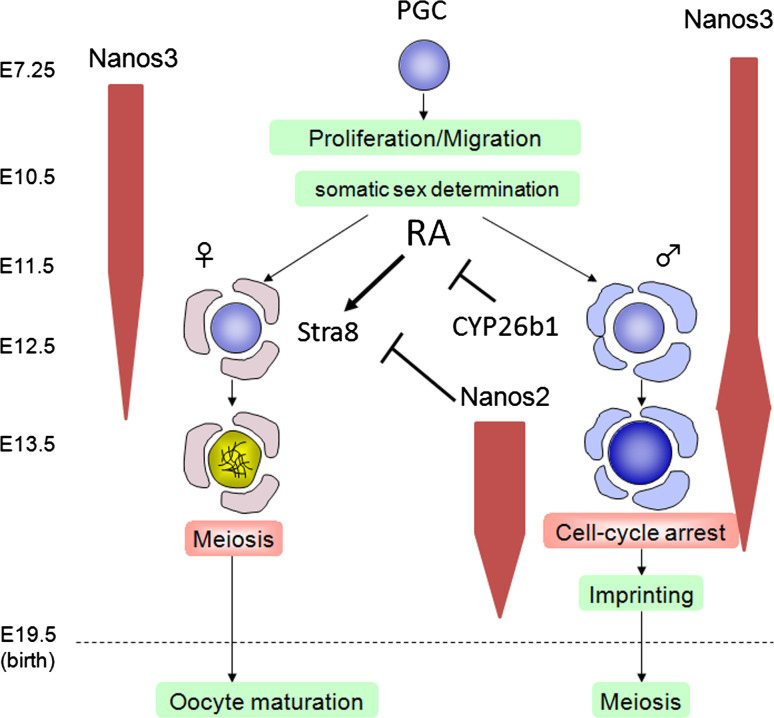
Fig. 1.
Developmental pathways involved in the sexual differentiation of germ cells. Once PGCs are formed, they proliferate and migrate toward the future gonads in which somatic cells commence sexual differentiation by expressing either male or female promoting factors. Retinoic acid (RA) is produced in both male and female gonads, but is destroyed by CYP26b1, which is specifically expressed in the male gonad. RA induces Stra8 expression in female germ cells, which then enter meiosis. In contrast, Stra8 expression is suppressed by RA degradation via Cyp26b1 and later by Nanos2 expression in germ cells. Male germ cells do not enter meiosis during embryogenesis. The expression of Nanos3 and Nanos2 is schematically indicated