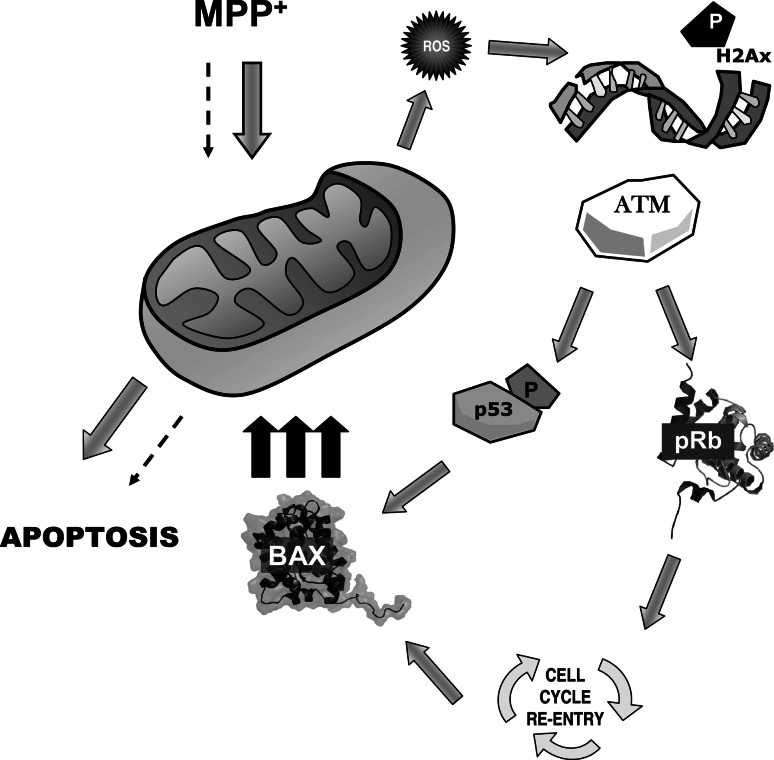
Fig. 12.
Intracellular pathways involved in MPP+-induced cell death in CGC cells. MPP+ induces an early mitochondrial alteration with an ROS increase which is not sufficient to induce apoptosis in cells. However, mitochondrial alteration (complex I inhibition) generated ROS, which induced DNA damage with an activation of enzymes involved in DNA repair such as ATM. Subsequently, ATM could activate downstream targets such as p53 or, as we suggest in the present manuscript, the modulation of pRb phosphorylation and regulate cell-cycle proteins implicated in the G1/S checkpoint, thus driving CGC cell-cycle re-entry or BAX induction. When BAX is over-expressed, it migrates toward the mitochondria and favors the apoptotic process via the release of pro-apoptotic proteins