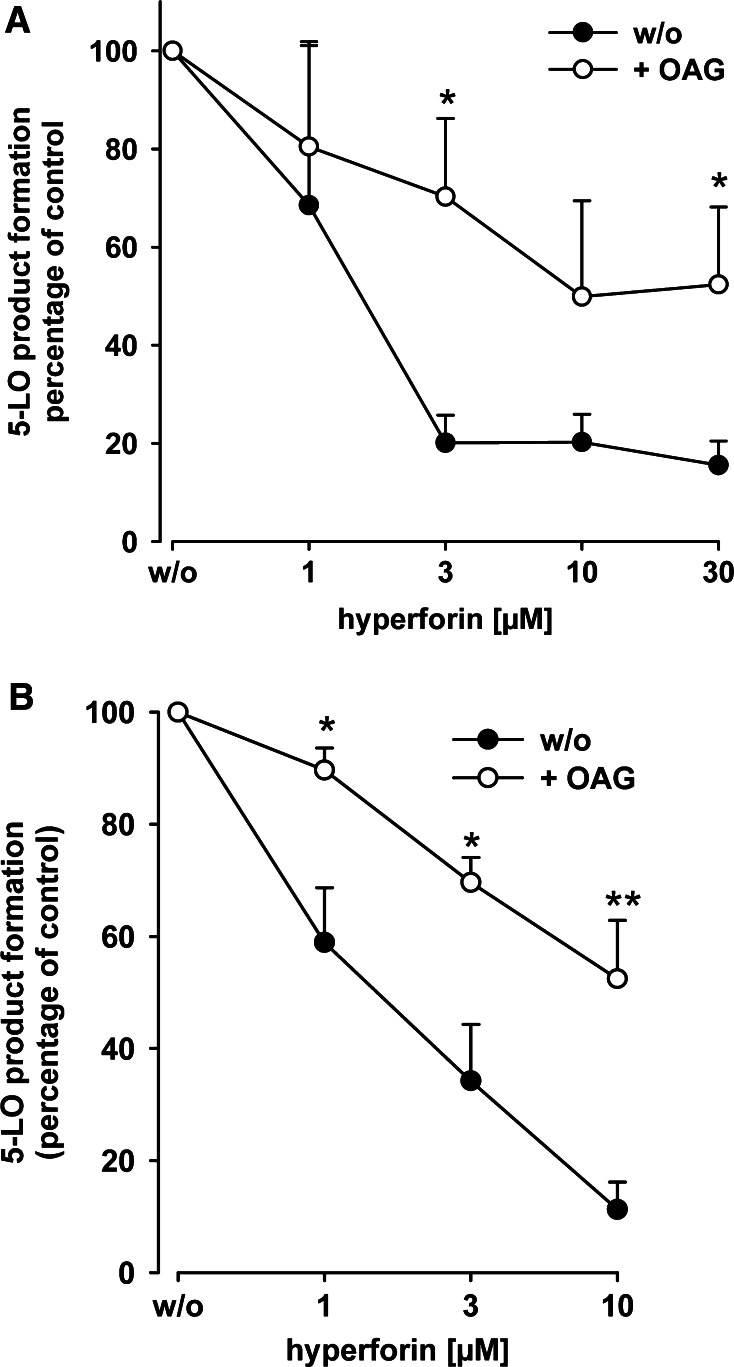
Fig. 6.
1-Oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (OAG) reduces the potency of hyperforin to inhibit 5-LO activity. a Effects of OAG on hyperforin-mediated 5-LO inhibition in intact neutrophils. Freshly isolated neutrophils (5 × 106) were resuspended in 1 ml PGC and pre-incubated with hyperforin (or DMSO as vehicle) for 15 min at 37°C at the indicated concentrations. OAG (30 µM) or solvent (DMSO, negative control) was added and, after another 3 min, neutrophils were challenged by ionomycin (1 µM) and AA (20 µM). The reaction was stopped after another 10 min and 5-LO product formation was determined. The 100% values correspond to 103 ± 6 (ionomycin) and 142 ± 31 (ionomycin + OAG) ng 5-LO products per 106 cells. b Partially purified human recombinant 5-LO (0.5 µg) expressed in E.coli was pre-incubated in 1 ml PG buffer plus 1 mM EDTA with hyperforin at the indicated concentrations or with vehicle at 4°C with or without 30 µM OAG. ATP (1 mM) was added, and, after 5–10 min, samples were prewarmed at 37°C for 30 s and 5-LO product formation was started by addition of 2 mM CaCl2 and 20 µM AA. After 10 min, 5-LO product formation was determined. The 100% values correspond to 5.3 ± 0.6 (w/o) and 4.4 ± 0.3 (+ OAG) µmol 5-LO products per mg protein. Values are given as mean + SE, n = 5; **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 versus controls without OAG (w/o) at corresponding concentrations of hyperforin