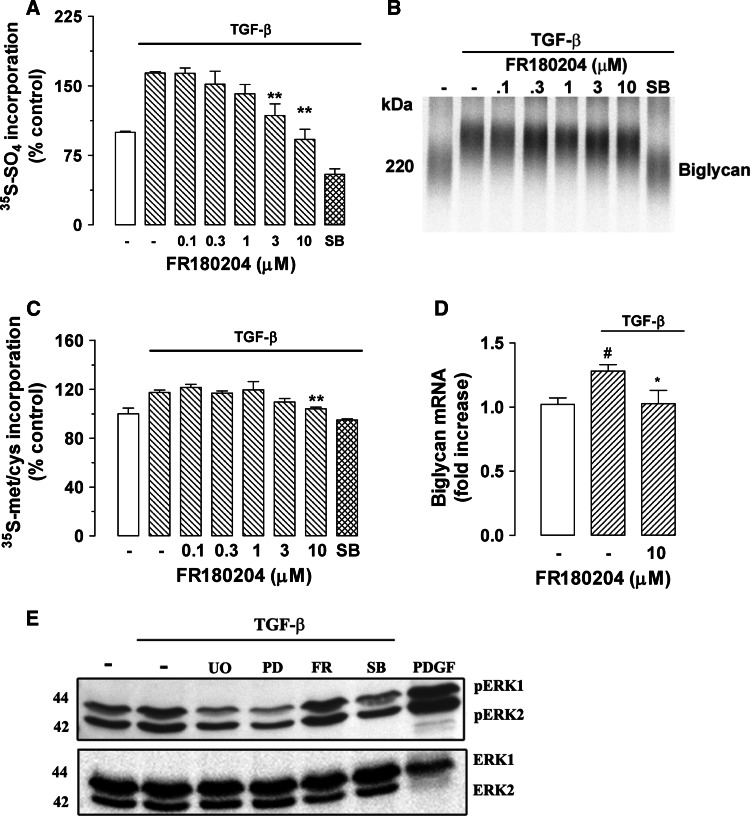
Fig. 3.
Determination of the role of ERK activity in TGF-β-mediated proteoglycan synthesis in human VSMCs using the direct ERK inhibitor FR180204. The ERK inhibitor blocks TGF-β-mediated GAG elongation in human VSMCs. VSMCs were treated with FR180204 (0.1–10 μM) in the presence of TGF-β (2 ng/ml) and [35S]-SO4 (50 μCi/ml) for 24 h. a [35S]-SO4 incorporation. b SDS-PAGE analysis. c [35S]-Met/Cys incorporation into proteoglycan core protein synthesis. d Biglycan mRNA expression was analyzed exactly as described in the legend of Fig. 1. e TGF-β/Alk 5-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation in human VSMCs. VSMCs were treated with TGF-β (2 ng/ml) and UO126 (3 μM), PD98059 (30 μM), FR180204 (10 μM) and SB431542 (3 μM) for 4 h. PDGF (50 ng/ml)-treated VSMCs for 4 h were used as positive control. Cell lysates were collected, and proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE on a 10% acrylamide gel and transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. The membrane was incubated with anti-phospho-ERK1/2 polyclonal antibody (1:1,000 dilution) overnight at 4°C followed by incubation with peroxidase-labeled anti-rabbit IgG (1:5,000 dilution) for 1 h at room temperature. The membrane was then probed with anti-ERK1/2 rabbit polyclonal antibody (1:1,000 dilution) for 1 h at room temperature followed by incubation with peroxidase-labeled anti-rabbit IgG (1:4,000 dilution) for 1 h. The Western-blot analysis is representative of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 versus treated control; **p < 0.01 versus treated control; # p < 0.05 versus untreated control