Fig. 2.
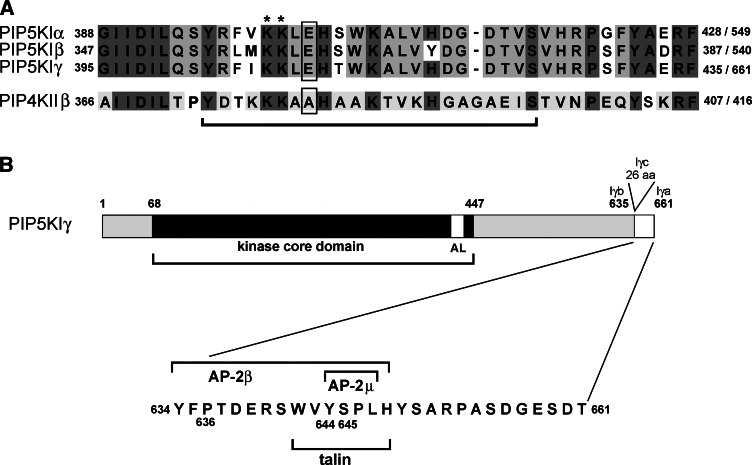
Organization of PIP5KI molecule. a Amino acid sequence of activation loop regions of human PIP5KIα, human Iβ, and murine Iγ (upper panel) and human PIP4KIIβ (lower panel). The first and the last amino acid of the regions as well as the total number of amino acids composing the proteins are indicated. Dark gray background marks amino acids conserved between PIP5KI and PIP4KII subfamilies; amino acids conserved only within the PIP5KI and PIP4KII subfamilies, but different between them are shown by the light gray background [22, 23, 59]. Bar below the alignment indicates regions exchanged between PIP5KIβ and PIP4KIIβ by Kunz et al. [56]. Asterisks indicate two lysine residues participating in membrane binding of PIPKs while glutamic acid residue and alanine residue determining substrate specificity of PIP5KI and PIP4KII, respectively, are marked by boxes. b A schematic representation of murine PIP5KIγa (661 amino acids) and PIP5KIγb (635 amino acids). PIP5KIγc of rodents is composed of 687 amino acids and contains a 26-amino-acid insert at Ph635 [23, 24]. AL, activation loop. In the lower panel, the amino acid composition of 26-amino-acid tail of murine PIP5KIγa is shown. The motifs engaged in the binding of talin, AP-2β and AP-2μ, are marked by bars. In human PIP5KIγa, two amino acids are inserted between Arg652 and Pro653 with the Arg652 exchanged for Glu652 [132]