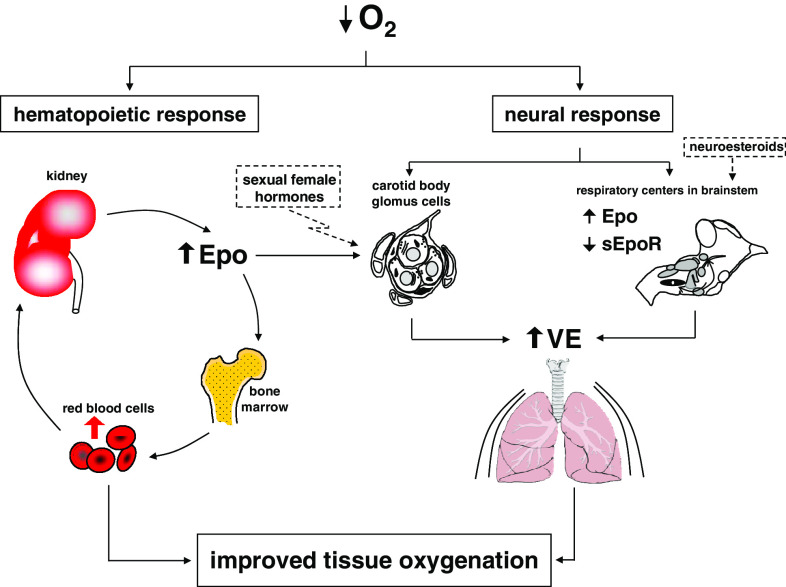
Fig. 3.
Model of ventilatory response to hypoxia showing the contribution of cerebral and plasma Epo. During the first minutes of hypoxia, carotid bodies sense the drop of arterial oxygen pressure thus leading to a fast response to hypoxia. Longer exposure to hypoxia promotes a higher secretion of Epo by the kidney. An increased level of plasma Epo augments the oxygen carrying capacity (by gradual increase of the hematocrit), but also contributes to the regulation of ventilation (VE) by regulating the activity of the carotid body glomus cells. In parallel, the level of cerebral Epo is increased in brainstem (and decreased the level of sEpoR), thus contributing to the regulation of central ventilation