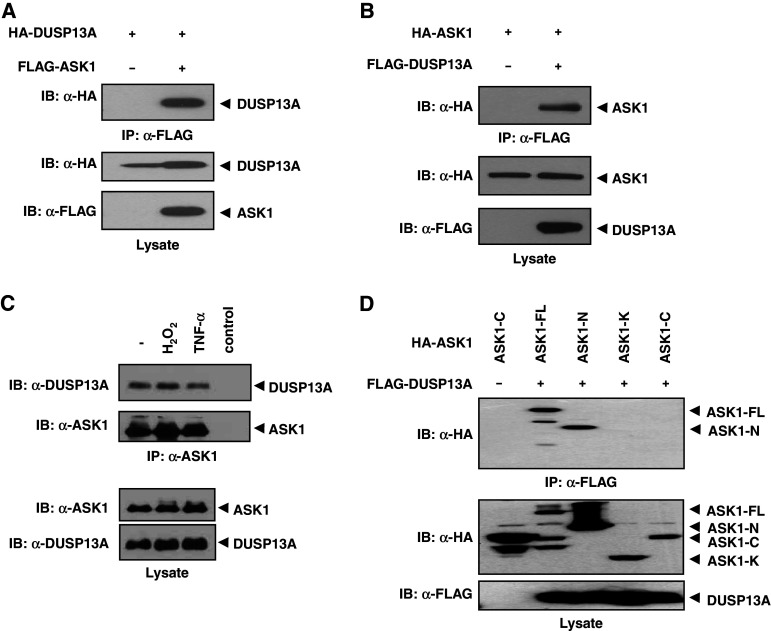
Fig. 1.
Interaction between ASK1 and DUSP13A. a HEK 293 cells were co-transfected using HA-DUSP13A with or without FLAG-ASK1. After 48 h of transfection, cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2-agarose. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with an anti-HA antibody (top). Middle and bottom panels show expression levels of HA-DUSP13A and FLAG-ASK1 in cell lysates, respectively. b HEK 293 cells were transfected using HA-ASK1 with or without FLAG-DUSP13A. Co-immunoprecipitation was carried out as described above. c Endogenous interaction between ASK1 and DUSP13A is independent of H2O2 and TNF-α. Lysates from SK-N-SH cells treated with H2O2 (1 mM, 1 h) or TNF-α (20 ng/ml, 1 h) were immunoprecipitated with anti-ASK1 (H-300) beads and immunoblotted with an anti-DUSP13A antibody or ASK1-specific antibody. The far right lane (control) shows the immunoblotting of anti-ASK1 (H-300) beads alone used in the immunoprecipitation to confirm no indigenous IgG reactivity. The levels of endogenous proteins were measured by appropriate antibodies. d DUSP13A preferentially interacts with the N-terminal domain of ASK1. HEK 293 cells were co-transfected with FLAG-DUSP13A and either HA-ASK1-WT or its deletion mutants, as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2-agarose. Immunoprecipitates and aliquots of each lysate were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-HA and anti-FLAG antibodies, as indicated. ASK1 apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1, ASK1-FL full-length ASK1, ASK1-N ASK1 N-terminal domain (residues 1–666), ASK1-K ASK1 kinase domain (residues 649–940), ASK1-C ASK1 C-terminal domain (residues 941–1375), DUSP13A dual-specificity phosphatase 13A, IgG immunoglobulin G, SDS-PAGE sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-α, HA hemagglutinin