Fig. 5.
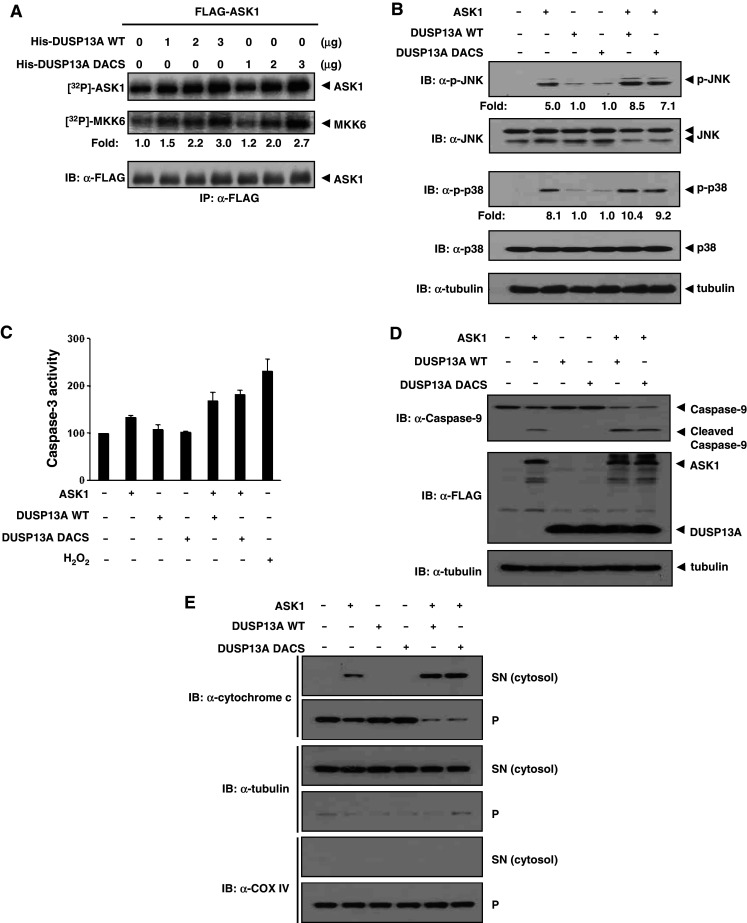
DUSP13A enhances ASK1 kinase activity and apoptosis in a manner independent of the phosphatase activity. a Autophosphorylation activity and in vitro kinase activity relative to the amount of ASK1 are shown as fold increase relative to that of FLAG-ASK1 from transfected HEK 293 cells. Top autophosphorylation assay of ASK1, middle in vitro kinase assay using His-MKK6 as a substrate, bottom immunoblotting of ASK1 with anti-FLAG-M2 antibody. b Overexpression of DUSP13A activates JNK1/p38 activity in the presence of ASK1. After transfection into MEF cells, cells were lysed with lysis buffer and immunoblotted by appropriate antibodies. c Activation of caspase-3 by DUSP13A in MEF cells. After 48 h of transfection, cells were lysed, and the caspase-3 activities in lysates were measured using DEVD-7-amino-4-methylcoumarin as a substrate. Cells treated with 1 mM H2O2 for 16 h were used as a positive control. Graphs represent the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate ± SEM. d Processing of caspase-9 is induced by ASK1 and DUSP13A. After 48 h of transfection, MEF cells were lysed and immunoblotted with anti-caspase-9 antibody. e DUSP13A enhances the ASK1-mediated release of cytochrome c into the cytosol. The release of cytochrome c into the cytosol of transfected MEF was determined by immunoblotting after separation of cytosol (SN) from other organelles (p). The presence of tubulin (cytosol marker) and COX IV (mitochondria marker) in each fraction was revealed by immunoblotting; p pellets, SN supernatants
