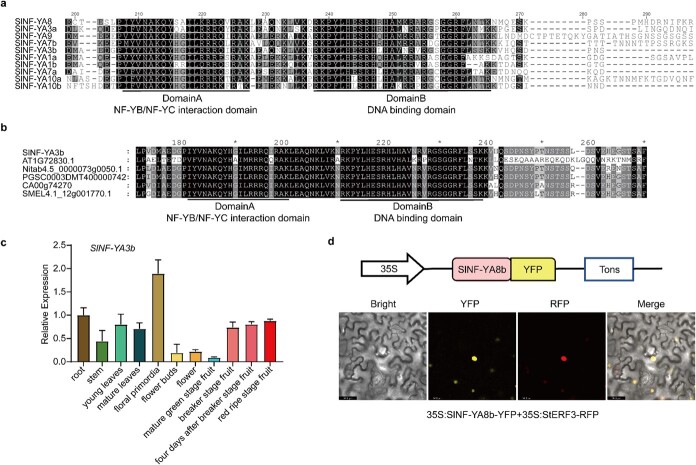
Figure 1.
Characterization of SlNF-YA3b. a, b Protein sequence alignments of 10 tomato NF-YA members (a) and representatives of NF-YA counterparts from other plant species (b). A highly conserved NF-YA region comprises Domain A and Domain B, which are underlined. Protein sequences of the 10 tomato NF-YA members (a) and their counterparts from other plants were obtained from GenBank and other databases, including protein sequences for tomato (SlNF-YA3b, Solyc12g009050.1), Arabidopsis (AT1G72830.1), pepper (CA00g74270), eggplant (SMEL4.1_12g001770.1), tobacco (Nitab4.5_0000073g0050.1), and potato (PGSC0003DMT400000742). c Relative expression levels of NF-YA3b in different tissues of WT plants. Each statistic is displayed as a mean value ± standard error (n = 3). d Subcellular localization of an NF-YA3b-YFP fusion protein. Diagram of the construct used for subcellular localization (upper panel). TNOS, transcription termination sequence of the Nopaline Synthase (NOS) gene. Potato Ethylene Responsive Factor 3 (StERF3) tagged with an RFP served as a nuclear localization marker (StERF3-RFP) and was co-expressed transiently with NF-YA3b-YFP in tobacco leaves. Confocal microscopy was used to capture the fluorescence images. Scale bars, 36.8 μm.