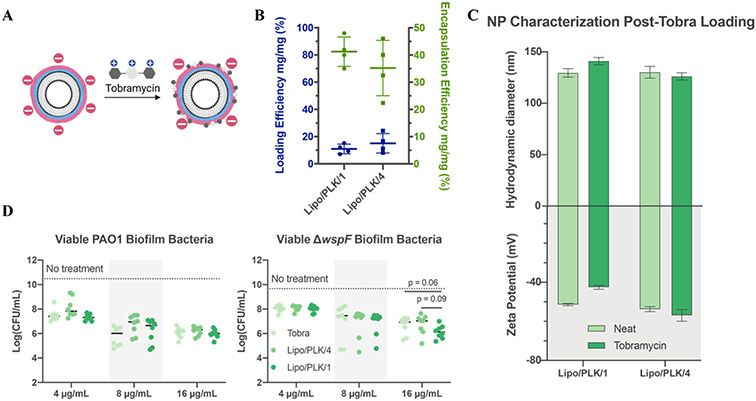
Figure 5.
Nanoparticle carriers loaded with tobramycin enhance antibiotic delivery. A) Schematic illustration of tobramycin electrostatically adsorbed into the final layer. B) Tobramycin absorbs onto each nanoparticle with satisfactory loading and encapsulation efficiency. N = 4 independent loading replicates, shown as an average and standard deviation. C) Nanoparticle size and zeta potential comparison before and after loading tobramycin show little difference. N = 3 technical replicates, shown as an average and standard deviation. D) Overnight biofilms treated with dose-matched tobramycin treatments had similar efficacy for PAO1, but a 3-fold reduction in colony-forming units in ΔwspF at the highest concentration. Dark lines in D, sometimes blocked by individual data points, represent the average log(CFU/mL) of biofilms treated with the medium control. N = 4 biological replicates using an independent nanoparticle formulation each with N = 2 technical duplicates. Statistics were calculated using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons correction, comparing means against Lipo/PLK/1.