Figure 2.
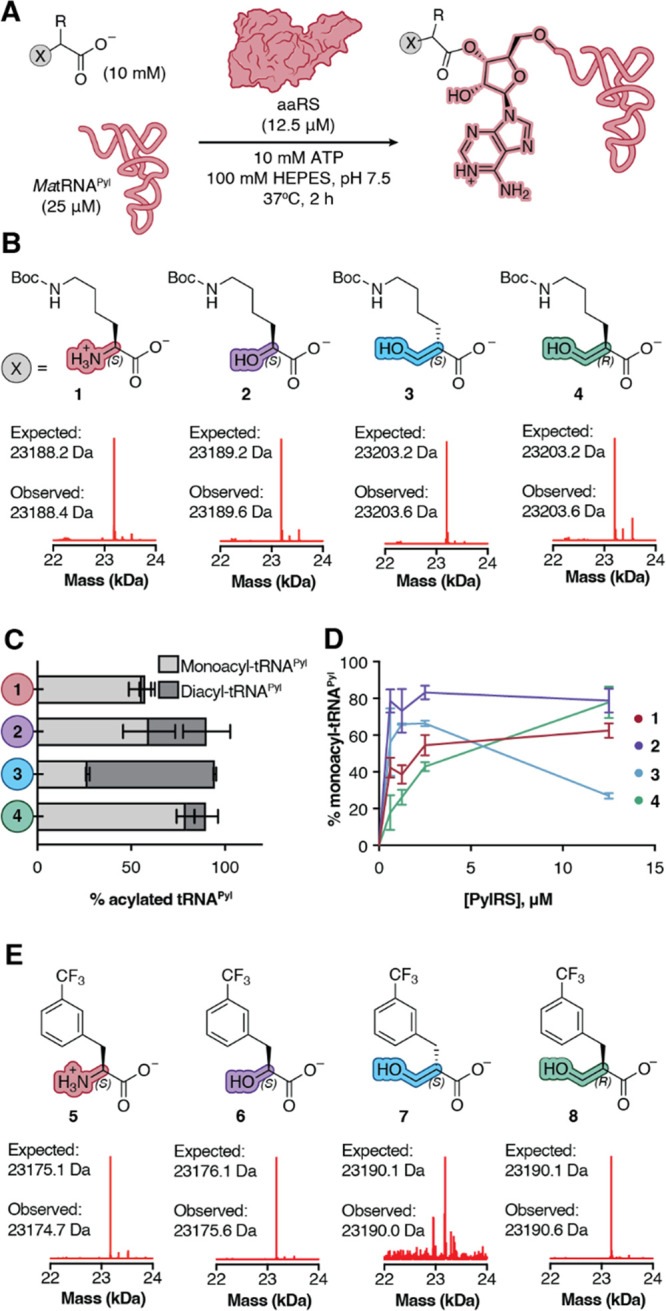
MaPylRS andMaFRSA acylate tRNAPyl with β2-hydroxy acid substrates in vitro. (A) Workflow for and (B) deconvoluted mass spectra of in vitro tRNAPyl acylation reactions containing 12.5 μM MaFRSA and supplemented with monomers 1–4. Signal is normalized to the highest signal in the respective traces. Expected masses shown correspond to monoacylated products. (C) Plot illustrating the relative yields of mono- and diacylated tRNAPyl generated during in vitro acylation reactions containing 12.5 μM PylRS and supplemented with 10 mM of monomer 1, 2, 3, or 4. (D) Plot illustrating yield of monoacylated tRNAPyl as a function of [MaPylRS]. The analogous plot showing the yield of mono- + diacylated tRNAPyl as a function of [MaPylRS] is shown in Supporting Information Figure 2. (E) Deconvoluted mass spectra of in vitro tRNAPyl acylation reactions containing 12.5 μM MaFRSA and supplemented with monomers 5–8. Signal is normalized to the highest signal in respective traces. Expected masses shown correspond to monoacylated products. Control tRNAPyl acylation reactions in which tRNAPyl, enzyme, or substrate is omitted are shown in Supporting Information Figures 1 and 3.
