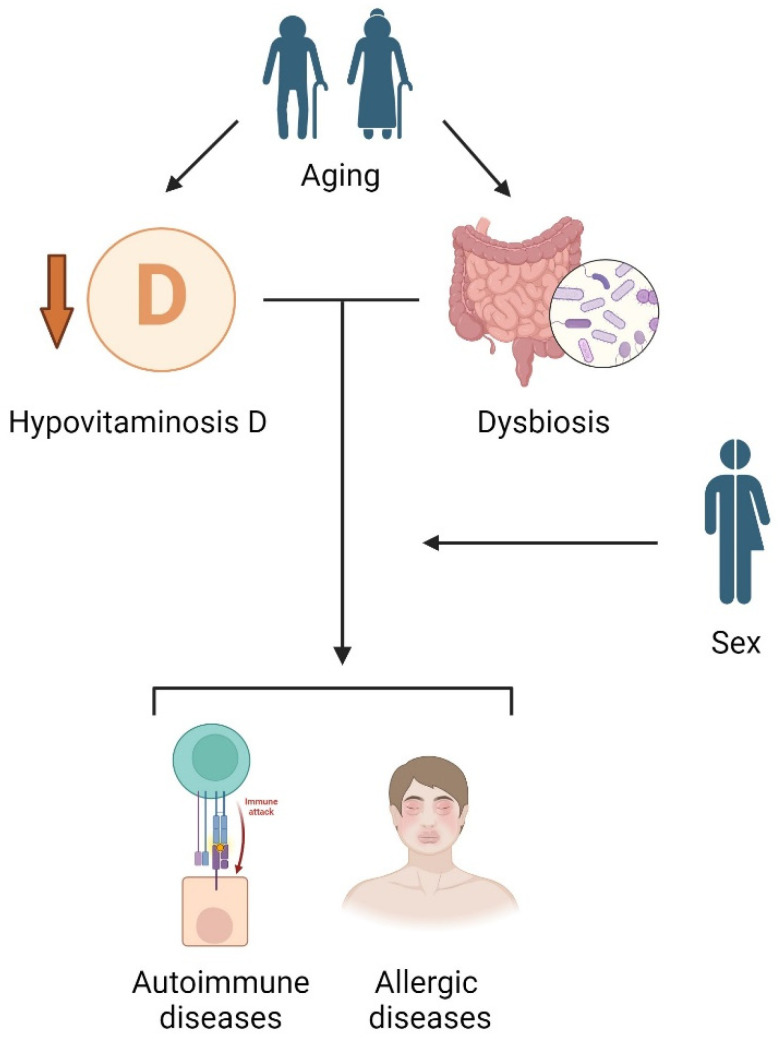
Figure 3.
Based on recent literature, we produced a possible explanatory scheme for the relationship between vitamin D, gut microbiome, sex, age, and immune-mediated diseases. The center of the model is characterized by the relevant and partly interdependent role of hypovitaminosis D and dysbiosis in the development of autoimmune or allergic diseases. In this scheme, age is a key aspect because it is a well-known risk factor for developing both vitamin D deficiency and alterations in the gut microbiome, while sex could mediate the effect of the above elements on the incidence and clinical course of immune-mediated diseases, with mechanisms yet to be specified in detail. Created with BioRender.com.