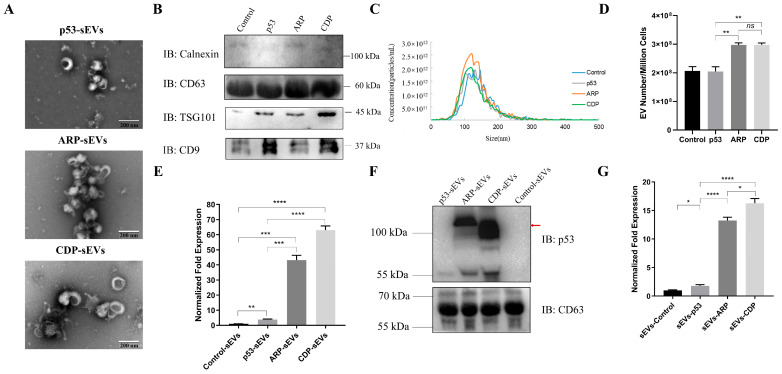
Figure 3.
Characterization of HEK293T-derived sEVs and enrichment analysis of p53 and its fusions in sEVs. (A) Electron micrographs display the characteristic cup-shaped and bilayered membrane structure of sEVs derived from HEK293T cells transfected with p53, ARP, or CDP expression constructs. Scale bar = 200 nm. (B) Western blot confirming the presence of EV marker proteins (CD63, TSG101, CD9) and the absence of cellular protein calnexin in sEVs from the different groups. sEVs from HEK293T cells transfected with the control vector (minipHrneo) served as controls. (C) The representative size distribution of HEK293T-sEVs from the different groups. (D) Quantitative analysis of HEK293T-derived sEVs produced per million cells across different groups (n = 3 per group, ** p < 0.01, ns, not significant). (E) RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA levels for p53 and its fusions in sEVs, indicating significantly higher levels in sEVs from the ARP and CDP groups compared to the p53 groups (n = 3 per group; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001). (F,G) Western blot analysis revealed markedly elevated fusion protein loading levels in the ARP and CDP groups compared to the p53 group. The red arrow highlights bands corresponding to fusion proteins. Quantification was performed by summing the intensities of all observed bands detected for p53, normalized against CD63 (n = 3 per group; * p < 0.05, **** p < 0.0001). Original images can be found in Supplementary Materials.