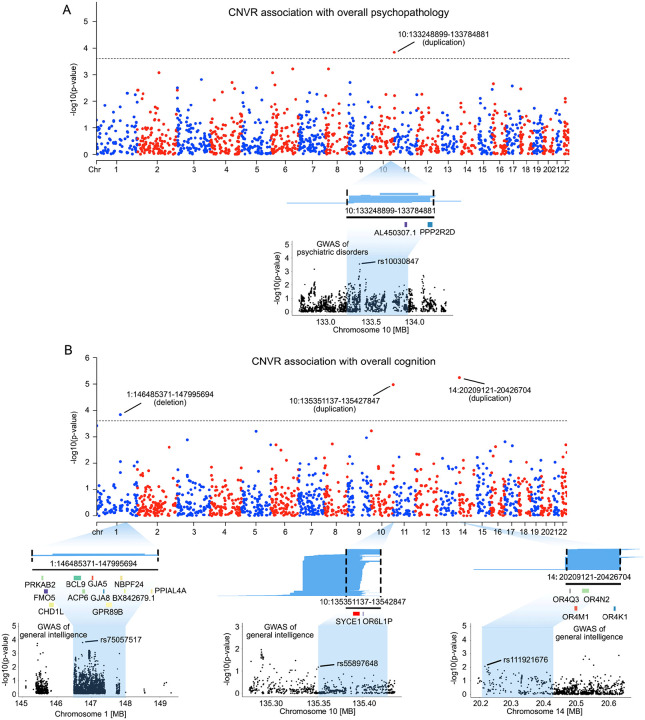
Figure 2. Genome-wide CNVRs associations with overall psychopathology and cognitive function.
(A) Genome-wide CNVR association with overall psychopathology. Manhattan plot illustrates significant CNVR associations with the overall psychopathology measure at Bonferroni-corrected p<2.5×10−4 (i.e., 5×10−4/2), the recommended threshold for genome-wide significance in the ParseCNV2 platform. Blue lines under the Manhattan plot represent the 16 duplications contributing to the significant CNVR association. The black line and the genes below them indicate the genomic position of genes encompassed by the CNVR significantly associated with psychopathology. The Manhattan plot at the bottom illustrates the GWAS association of psychiatric disorders with common genetic variants (i.e., SNPs) within the identified CNVR, as reported by Romero et al49. (B) Genome-wide CNVR association with global cognitive function. Three CNVRs were found significantly associated with the overall cognitive function at Bonferroni-corrected p<2.5×10−4 (i.e., 5×10−4/2). Blue lines under the Manhattan plot represent the CNVs that contribute to each significant CNVR association. The black lines and the genes below them indicate the genomic position of genes encompassed by the CNVR significantly associated with global cognitive function. The Manhattan plot at the bottom illustrates GWAS SNP associations with general intelligence within each CNVR, as reported by Savage et al.50.