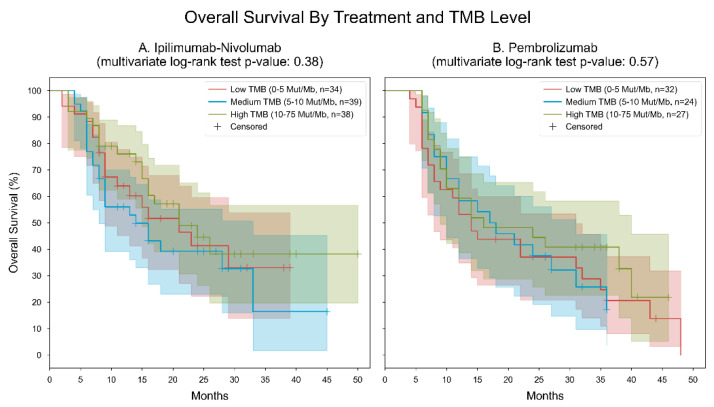
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier curves for overall survival, stratified by treatment and TMB level. Patients were divided into 6 subgroups based on their measured TMB level (low: “0–5” mut/MB, medium: “5–10” mut/Mb, high: “10–75” mut/Mb) and the type of immunotherapy they received (ipilimumab-nivolumab or pembrolizumab). Two separate analyses were performed, one for patients with ipilimumab-nivolumab and the other for patients with Pembrolizumab. Cohort (A). Ipilimumab-Nivolumab. In the low TMB group, the median overall survival was 21 months; in the medium TMB group, the median overall survival was 14 months; in the high TMB group, the median overall survival was 21 months. The p-value of the multivariate log-rank statistic for survival difference between the three groups was 0.38. In a Cox proportional hazards (PH) model for patients treated with ipilimumab-nivolumab, which included terms for TMB levels, the low TMB level was associated with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.23 (95% CI [0.64, 2.31], p = 0.53) compared to the high TMB level; the medium TMB level was associated with an HR of 1.54 (95% CI [0.84, 2.82], p = 0.16) compared to the high TMB level.; Cohort (B). Pembrolizumab. In the low TMB group, the median overall survival was 14 months; in the medium TMB group, the median overall survival was 17 months; in the high TMB group, the median overall survival was 16 months. The p-value of the multivariate log-rank statistic for survival difference between the three groups was 0.57. In a Cox proportional hazards (PH) model for patients treated with pembrolizumab, which included terms for TMB levels, the low TMB level was associated with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.37 (95% CI [0.74, 2.51], p = 0.31) compared to the high TMB level; the medium TMB level was associated with an HR of 1.31 (95% CI [0.67, 2.53], p = 0.43) compared to the high TMB level.