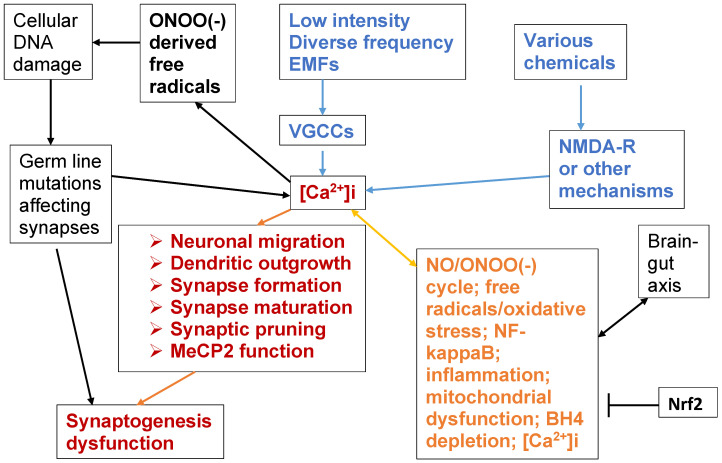
Figure 1.
Proposed central set of mechanisms causing autism spectrum disorders by acting during the perinatal period (before and after birth), to impact synaptogenesis which normally occurs at very high rates. The most central mechanism is excessive intracellular calcium [Ca2+]i which causes abnormal regulation of each of the six mechanisms just below center left, each of which are essential to synaptogenesis. Each of those six mechanisms are regulated by [Ca2+]i. Electronically-generated EMFs activate the VGCC calcium channels in the plasma membrane, producing large calcium influxes and therefore large increases in [Ca2+]i. Each of the 15 chemicals, or groups of chemicals, that are thought to have roles in ASD causation also act to increase [Ca2+]i. The NO/ONOO(-) cycle mechanism, on the lower right side, is proposed to have a major role in producing the chronicity of ASDs.