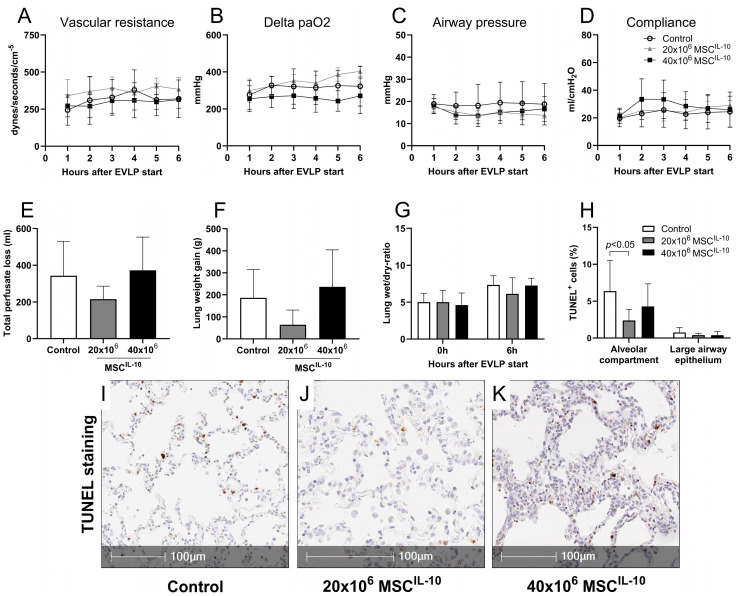
Figure 3.
Lung function during EVLP after MSCIL-10 administration. Pig lungs with 24 h cold ischemia were connected to clinical-grade EVLP and randomized to control (n = 7), or to receive 20 × 106 (n = 5) or 40 × 106 MSCsIL-10 (n = 6) through the pulmonary artery 1 h after EVLP start. Lung function parameters were recorded every hour for 6 h. (A) Pulmonary vascular resistance, (B) delta pO2, (C) peak airway pressure and (D) dynamic compliance. Vascular permeability and lung edema were evaluated by (E) total perfusate loss and (F) lung weight gain during EVLP, and by (G) lung wet/dry ratio at the end of EVLP. Cellular apoptosis was evaluated from tissue sections at the end of EVLP by (H) TUNEL staining using automated image analysis and tissue segmentation to alveolar and large airway epithelium compartments. Representative TUNEL+ staining of (I) control, (J) 20 × 106 and (K) 40 × 106 MSCIL-10 lungs. Data mean ± SD, analyzed by 2-way ANOVA (A–D,G,H) or 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s correction (E,F) comparing treatment groups to the control group. EVLP, ex vivo lung perfusion; IL-10, interleukin-10; MSCs, mesenchymal stromal cells; PA, pulmonary artery; TUNEL, deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated deoxy uridine triphosphate nick-end labeling.