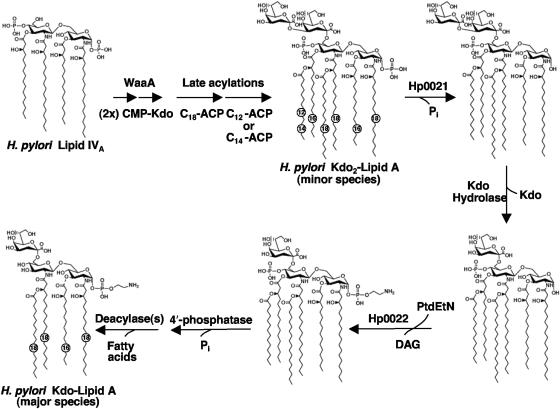
FIG. 1.
Proposed biosynthesis and modification of H. pylori Kdo2-lipid A. Following synthesis of lipid IVA, H. pylori WaaA transfers two Kdo sugars to the distal glucosamine of lipid A. Based upon the lipid A biosynthetic pathway of E. coli, this would be followed by the addition of the acyloxyacyl-linked fatty acyl chains, resulting in a lipid A species that can be detected as a minor component of H. pylori LPS (27, 38, 39). Following the constitutive biosynthetic pathway (the Raetz pathway), H. pylori Kdo2-lipid A is then modified by several enzymes. First, Hp0021 catalyzes the removal of the 1-phosphate group from H. pylori lipid A on the periplasmic side of the inner membrane (41). Other modifications include the removal of the outer Kdo sugar reported herein or the addition of a pEtN residue to the 1 position catalyzed by Hp0022 (41), both of which require prior removal of the 1-phosphate group. Additional enzymatic activities that are thought to be necessary for modification of H. pylori lipid A include a 4′-phosphatase (A. X. Tran and M. S. Trent, unpublished data) and at least one deacylase (C. M. Stead and M. S. Trent, unpublished data).