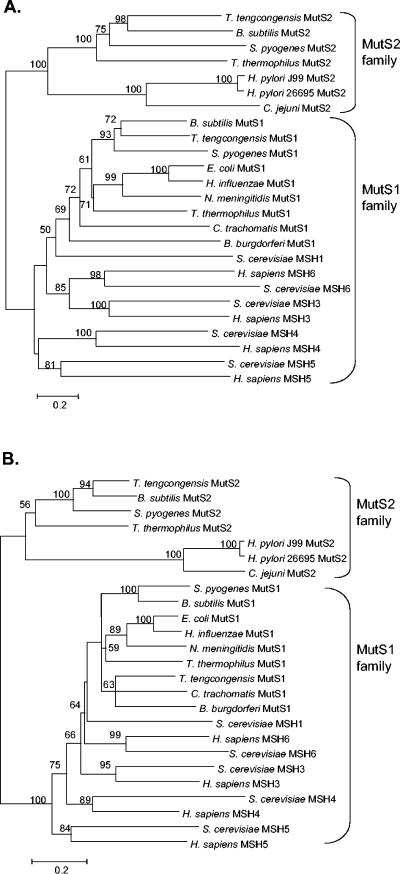
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of MutS family domains. A. The DNA association domain, conserved throughout MutS homologs, was identified using the SMART database (42), where it is annotated as MutSd. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the amino acid sequences of MutS1 from nine representative bacterial species, MutS2 from six representative bacterial species, and MSH2 to MSH6 from S. cerevisiae and H. sapiens (Table 3). B. subtilis, S. pyogenes, and T. tengcongensis were selected, since they possess both MutS1 and MutS2. The program Mega 2.1 (38) was used to construct the phylogeny, by using the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. B. The ATPase/dimerization domain, highly conserved throughout MutS homologs, was identified by using the SMART database (42), where it is annotated as MutSac. A phylogenetic tree was constructed as in panel A, with 1,000 bootstrap replicates.