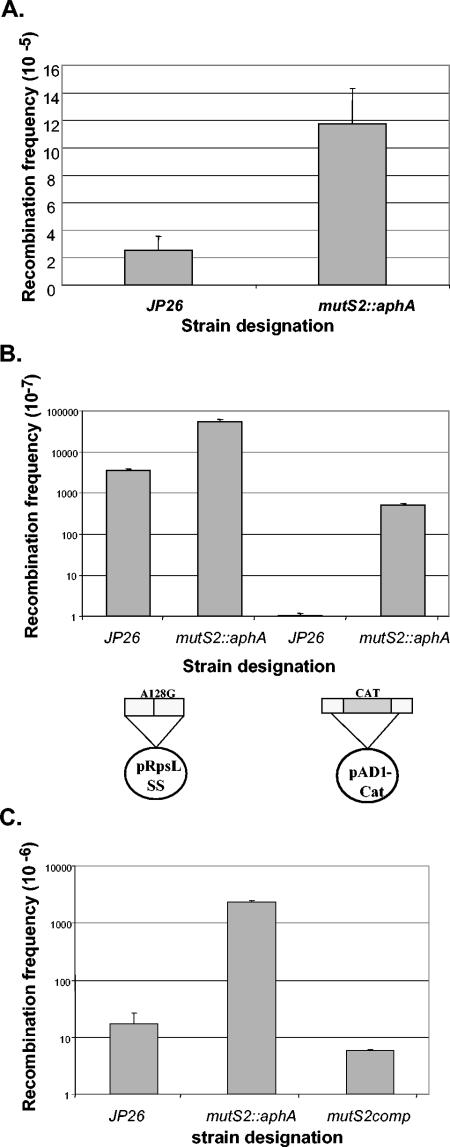
FIG. 4.
Intergenomic recombination frequencies of H. pylori wild-type and mutant strains using chromosomal, plasmid, or PCR product DNA. A. H. pylori strains JP26 and JP26/mutS2::aphA were transformed to streptomycin resistance by using chromosomal DNA from Str 26696, which has a point mutation (A128G) in the rpsL gene. Bars represent the means of four experiments. The mutS2::aphA mutant shows a significantly (P < 0.05) higher transformation frequency than wild-type JP26. B. H. pylori strains JP26 and mutS2::aphA were transformed with either pRpsLSS, which contains the 800-bp A128 rpsL fragment, or pAD1-CAT, which contains the ureAB promoter and downstream regions interrupted by a chloramphenicol resistance cas-sette, as shown in the schematic. For both pRpsLSS and pAD1-Cat donor DNA, the mutS2::aphA strain was transformed at a significantly (P < 0.05) higher frequency than wild-type JP26. Overall, pRpsLSS transforms both the wild-type and mutS2 mutant strains at 2 to 3 log10 higher frequency (P < 0.05) than pAD1-Cat. C. H. pylori strains JP26, mutS2::aphA, and mutS2comp were transformed to streptomycin resistance with an 800-bp A128G rpsL PCR product; bars represent the means of four to eight replicate experiments. The mutS2::aphA strain shows a 2 log10 higher transformation frequency (P < 0.05) than wild-type JP26. Complementation of JP26 mutS2::aphA with mutS2 in trans restored the recombination frequency to a level not significantly different from wild-type JP26.