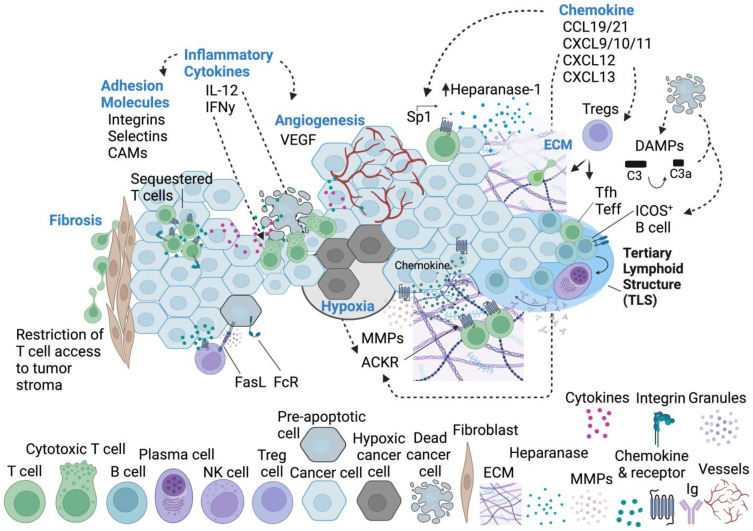
Figure 3.
Lymphoid cell recruitment to tumors by multiple mechanisms. Immune cell migration through ECM, tissue, blood, and lymphatics is highly dependent on expression of integrins, selectins, and cell adhesion molecules such as ICAM family ligands. Chemoattractants produced within the TME recruit and retain lymphocytes, which play a significant role in tumor elimination. Chemokine receptor expression on immune cells and tumor cells is highly dynamic. Tumors may alter chemokine receptor and cell adhesion factor expression to sequester or restrict T cell access within tumor stroma, limiting their effector capability. Inflammatory cytokines from immune cells or tumor/tumor associated cells can induce additional alterations to these cell surface molecules. Furthermore, inflammatory cytokines can promote T cell cytotoxicity, causing tumor cell apoptosis. These cytokines can also promote angiogenic programs, increasing flow of nutrients to the tumor, as well as myeloid derived suppressor cells (not pictured). Angiogenic programs can result in aberrant vasculature patterns, resulting in hypoxic tumor regions with limited effector cell presence. TME factors can also induce the expression of atypical chemokine receptors, which scavenge free ligands, disrupting intratumoral immune cell signaling and activation, as there is less bioavailable chemokine for typical receptors. Chemokine and cytokine expression patterns can also cause alternations to the ECM through induction of MMPs or heparanase-1, which can both promote or disrupt immune cell migration depending on the context. Chemokines also recruit Treg cells to the tumor which can induce immunosuppression. DAMPs from apoptotic cancer cells can activate complement signaling cascades and recruit B cells. Interactions between Tfh and B cells promote tertiary lymphoid structure formation, which supports the antitumor response. Furthermore, within tertiary lymphoid structures, interactions with antigen, B cells, and Tfh give rise to plasma cells, which produce large amounts of Igs. NK cells also contribute to immunosurveillance within the TME through recognition of Fas Ligand (FasL), Fc receptors, or TRAIL, though tumor cells have evolved mechanisms to downregulate those receptors to evade antitumor immune surveillance. Fibroblast remodeling contributes to tumor fibrosis, and may disrupt immune cell migration patterns or tumor access. Tfh, T follicular helper cell; Teff, effector T cell; Tregs, regulatory T cells; MMPs, matrix metalloproteases; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; Ig, Immunoglobulin.