Table 8.
Tests of Correlations between Neutron-capture and Sodium Abundance Ratios
| Sample | [Ba/Fe]+[Na/Fe] | [Eu/Fe]+[Na/Fe] | [Zr/Eu]+[Na/Fe] |
|---|---|---|---|
| This paper: all stars | (0.62, 28, 0.00048) | (0.49, 28, 0.0087) | (−0.53, 28, 0.0037) |
| This paper: r-process only | (0.56, 20, 0.0097) | (0.52, 20, 0.018) | (−0.59, 20, 0.0064) |
| Sneden et al. (1997) a | (0.46, 17, 0.066) | (0.21, 17, 0.43) | ⋯ |
| Sneden et al. (2000b) | (0.40, 31, 0.026) | ⋯ | ⋯ |
| Sobeck et al. (2011) a | (0.52, 8, 0.19) | (0.11, 8, 0.79) | (−0.0080, 7, 0.99) |
| This paper: Eu-rich stars | (0.47, 20, 0.03) | (0.15, 20, 0.53) | (−0.28, 20, 0.22) |
| This paper: Eu-poor stars | (0.44, 8, 0.28) | (0.46, 8, 0.25) | (−0.48, 8, 0.22) |
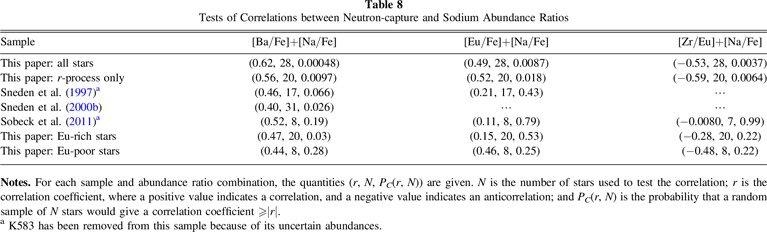
Notes. For each sample and abundance ratio combination, the quantities (r, N, P C (r, N)) are given. N is the number of stars used to test the correlation; r is the correlation coefficient, where a positive value indicates a correlation, and a negative value indicates an anticorrelation; and P C (r, N) is the probability that a random sample of N stars would give a correlation coefficient ≥∣r∣.
K583 has been removed from this sample because of its uncertain abundances.
