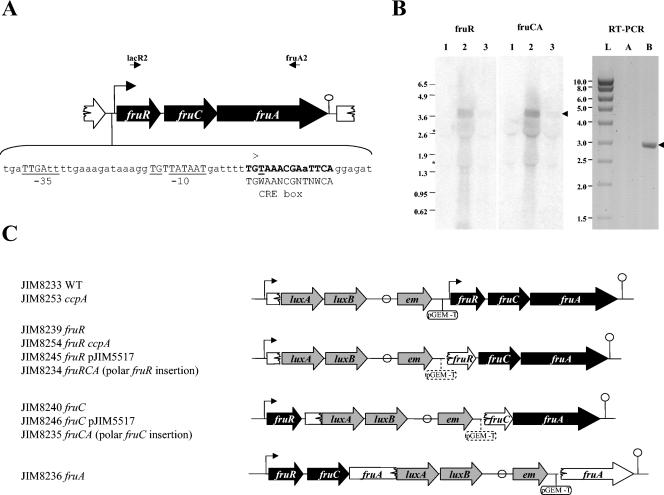
FIG. 1.
(A) Genetic organization of the L. lactis IL1403 fructose operon. fruR encodes a protein homologous to a transcriptional regulator, fruC, a 1-phosphofructokinase, and fruA, a fructose-specific enzyme II (EIIABC components). The transcriptional start point (+1) determined by 5′-RACE and the corresponding −10 and −35 boxes are indicated and underlined. A putative rho-independent terminator is indicated by a circle. A putative CRE box is shown in bold. The primers lacR1 and fruA2 are shown by arrows. (B) Northern blot with fruR (lacR2-lacR3) and fruCA (lacC1-fruA2) probes and, right panel, PCRs on the fructose gene transcripts using primers complementary to fruR (lacR2) and fruA (fruA2). RNAs were prepared from IL1403 cells grown in CDM-glucose (lane 1), CDM-fructose (lanes 2, A, and B), and CDM-glucose-fructose (lane 3). Lane L, Smart ladder (Promega), sizes of which are indicated in the left margin; lane A, PCR on 500 ng of RNA; lane B, RT-PCR on 500 ng of RNA diluted 40-fold. The asterisks on the left of the Northern blot indicate the positions of 16S and 23S RNAs that produced slightly artifactual bands. Arrows to the right of the panel indicate the position of the expected band corresponding to the fruRCA transcript (3.7 kb) and RT-PCR product (3 kb). (C) Schematic representation of inserted constructions in the fru operon and the corresponding strains used in this study. The promoter of the fru operon (Pfru) is indicated by an arrow. A putative rho-independent terminator is indicated by a circle. Genes of the fru operon are shown either in black when they are intact or in white when they are inactivated. The inserted genes are represented in gray. The pGEM-T plasmid is indicated by a line and a circle in either full features, when it is present in all the constructions, or in stippled features when it is not present in all the constructions.