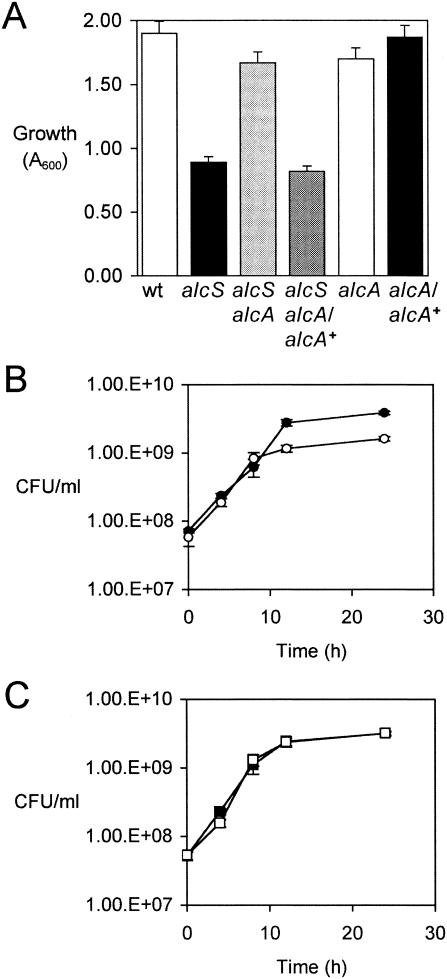
FIG. 6.
Iron starvation growth defect of alcS mutants is related to alcaligin production. (A) The bars indicate the mean growth yields of B. bronchiseptica strains, expressed as A600, and the error bars indicate standard deviations (n = 3) after 24 h of culture in iron-depleted SS batch cultures. Note that the growth of all strains was limited by the availability of only trace amounts of iron in this culture system, but alcaligin production by alcaligin-positive strains was maximized. Abbreviations for strains used are as follows: wt, B013N; alcS, BRM16; alcS alcA, BRM27; alcS alcA/alcA+, BRM27(pBB21); alcA, BRM26; alcA/alcA+, BRM26(pBB21). (B) Growth curves for B. bronchiseptica strains cultured in iron-depleted SS. Viable cell counts, expressed as CFU/ml (means ± standard deviations; n = 3), are shown. •, B013N (wild type); ○, BRM16 (alcS). (C) Growth curves for B. bronchiseptica strains cultured in iron-depleted SS. ▪, BRM26 (alcA); □, BRM27 (alcS alcA).