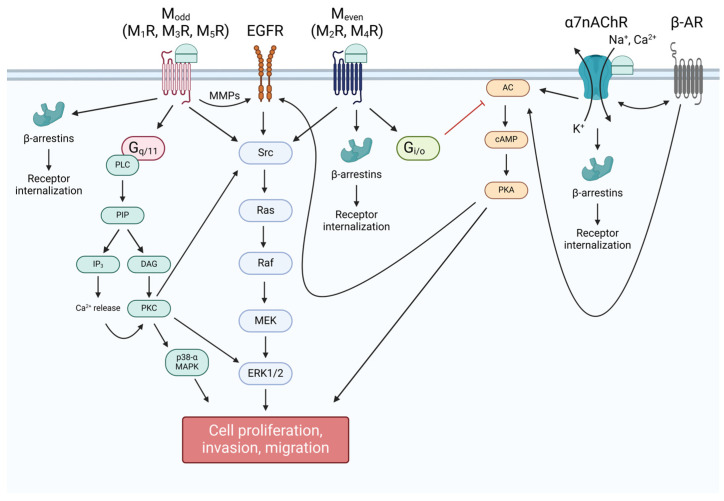
Figure 2.
Overview of post-receptor acetylcholine (ACh) signaling. Odd-numbered muscarinic receptors (Modd: M1R, M3R, and M5R) are coupled to Gq/11 signaling, which effects cellular change via phospholipid metabolism and increasing intracellular calcium concentrations, while even-numbered muscarinic receptors (Meven: M2R and M4R) are coupled to Gi/o, which inhibits the formation of cAMP by membrane-bound adenylyl cyclase (AC). As a result of Meven signaling, protein kinase C (PKC) is activated, which further activates mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK), such as p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and extracellular signal-related kinase-1/2 (ERK1/2), to alter gene expression. ACh-bound Modd also transactivates epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) via activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP), offering another mechanism whereby ERK1/2 can be activated. Meven activation is not known to directly transactivate EGFR, and instead leads to the inhibition of the activation of EGFR by protein kinase A (PKA). Nicotinic signaling is diverse and subtype-dependent. α7nAChR activates AC, leading to upregulation of cAMP production and PKA activation, both directly and through interplay with β-adrenergic receptors (β-AR). Muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic receptors can also recruit β-arrestins, which mediate receptor internalization. Created with BioRender.com.