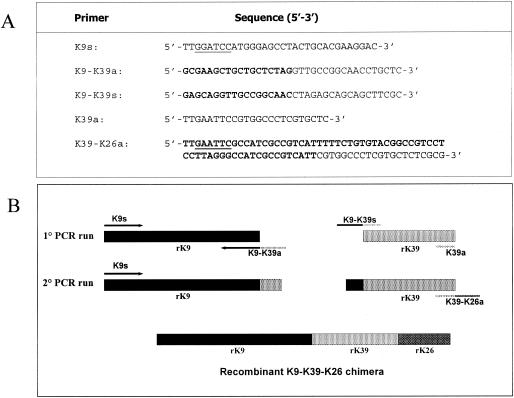
FIG. 1.
A: primer sequences used for amplification and joining of the K9-K39-K26 synthetic gene. Primer K9-K39a contains at the 5′ end an 18-bp sequence overlapping to the 5′ end of K39 sequence (bold). Primer K9-K39s contains at the 5′ end an 18-bp sequence overlapping to the 3′ end of K9 sequence (bold). The antisense primer K39-K26a contains a 5′ extension complementary to the sequence coding for 19 aa identified from K26 epitope mapping. (bold). Restriction sites BamHI (sense) and EcoRI (antisense) are underlined. B: PCR strategy used for joining of K9, K39sub, and K26 sequences. The primer set K9s/K9-K39a and K9-K39s/K39a were used in the first PCR step to produce two overlapping fragments. Purified amplicons were joined together in the second step using external primers K9s and K39-K26a.