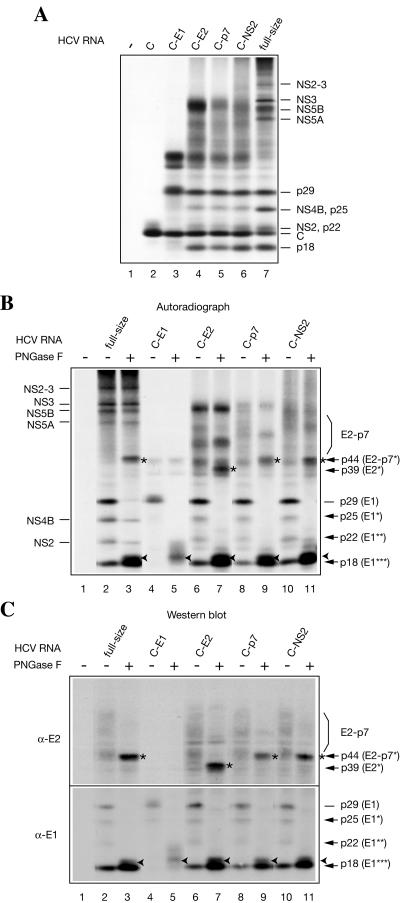
FIG. 4.
Products of subgenomic HCV RNA translation and identification of HCV glycoproteins. pCV-H77C was used as a template for DNA amplifications and subsequent synthesis of the subgenomic HCV RNAs as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Subgenomic HCV RNAs harboring the terminator codons after the core (C), E1 (C-E1), E2 (C-E2), p7 (C-p7), and NS2 (C-NS2) coding regions and full-size HCV RNA were translated in Krebs-2 S10 under standard conditions. Translation products were analyzed by SDS-15% PAGE and autoradiography. The positions of HCV-specific proteins are indicated on the right. (B) Autoradiograph of the full-size and subgenomic HCV RNA translation products that were incubated in either the absence (−) or presence (+) of PNGase F, as indicated. Nonstructural HCV proteinsare indicated on the left and HCV glycoproteins on the right of the autoradiogram. Asterisks and arrowheads indicate PNGase-deglycosylated E2-p7/E2 and E1, respectively. E1* and E1** are putative hypoglycosylated forms and E1*** is an unglycosylated form of E1 produced in the course of HCV RNA translation. (C) Products of translation of HCV RNAs shown in panel B were blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with the antibodies against HCV E2 and E1 glycoproteins, as indicated. In panels A to C in lanes 1, no mRNA was added to the reaction samples.