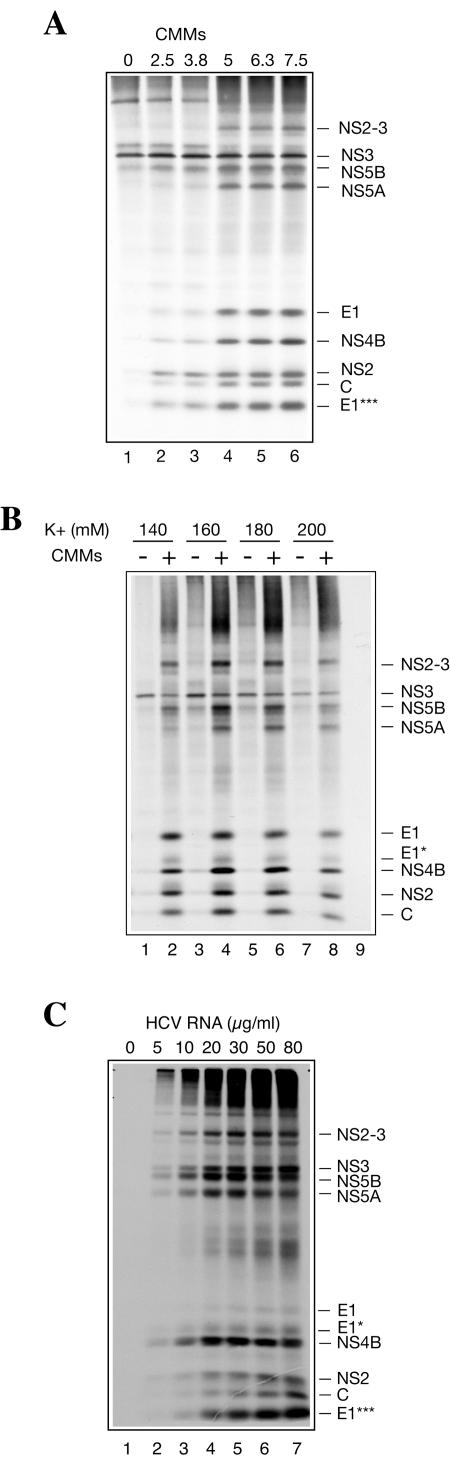
FIG. 5.
CMMs (A), potassium ion (B), and HCV RNA (C) concentration dependences of HCV protein synthesis in Krebs-2 S10. (A) HCV RNA was translated in the presence of the indicated amounts of CMMs (given as percent [vol/vol] of the total reaction volume) as described in the legend to Fig. 1. (B) Potassium ion concentration optimum of translation. Mg2+ was used at the optimal (2.5 mM) concentration. CMMs were present (+) in the reactions at 5% of the reaction volume where indicated. In lane 9, no HCV RNA or CMMs were added to the reaction sample containing 160 mM potassium ion concentration. (C) The indicated concentrations of HCV RNA were translated in the presence of CMMs (at 5% reaction volume) under optimal ionic conditions (160 mM K+ and 2.5 mM Mg2+). Other conditions were as specified above. The samples were analyzed by SDS-15% (A and C) or 10% (B) PAGE and autoradiography. The positions of HCV-specific proteins are indicated on the right.