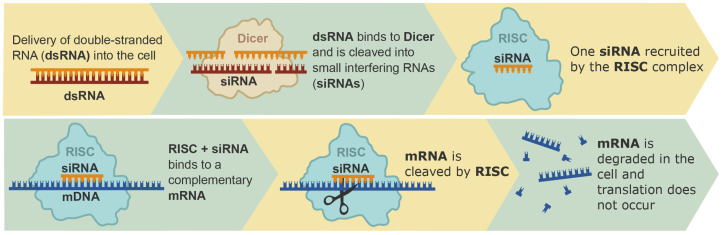
Figure 2.
Scheme of the RNA interference (RNAi) process. After the delivery of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) into the cell, the dsRNA is further cleaved into small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) by the ribonuclease Dicer. Then, siRNA binds with the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). RISC uses this siRNA to establish homologous RNAs in the cells, which triggers the endo-nucleolytic cleavage and translational inhibition of the cognate target mRNA, thereby leading to gene silencing.