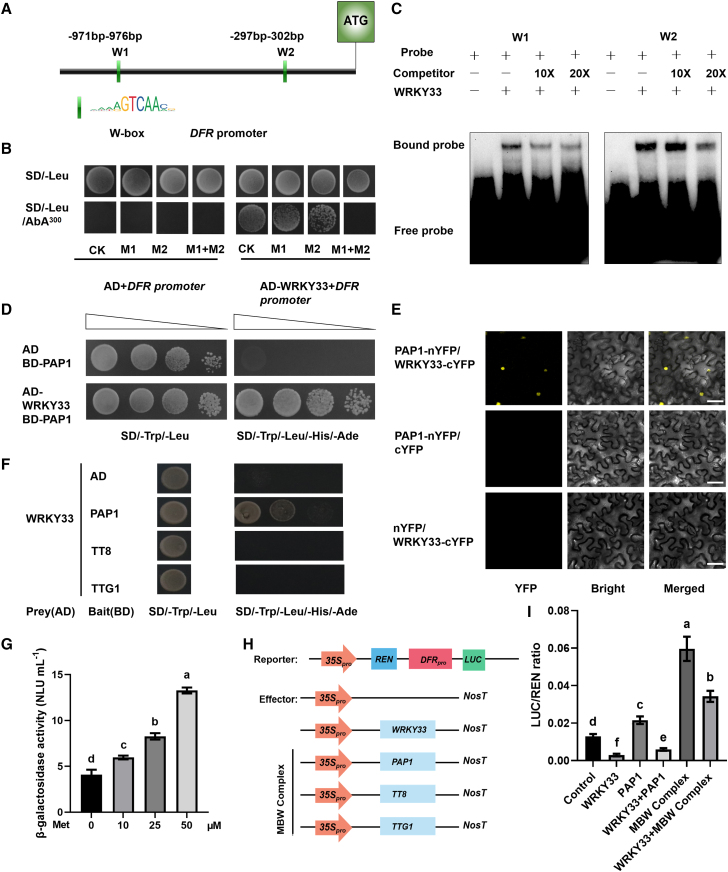
Figure 2.
WRKY33 directly and indirectly regulates DFR expression.
(A) Schematic diagram of the DFR promoter and its W-box motifs.
(B) Yeast one-hybrid assay showing that WRKY33 directly binds to a specific region of the DFR promoter. CK, the original sequence of the DFR promoter; M1, sequence with a mutation of the W box in region 1 of the DFR promoter (−971 to −976 bp from ATG); M2, sequence with a mutation of the W box in region 2 of the DFR promoter (−297 to −302 bp from ATG). The W box was replaced with “AAAAA.”
(C) EMSA indicating the binding of WRKY33 to the DFR promoter in vitro.
(D) Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assay showing that PAP1 interacts with WRKY33. The empty vector pGADT7 was used as a negative control.
(E) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay indicating the interaction between PAP1 and WRKY33 in vivo. The N-terminal fragment of YFP (nYFP) was fused to PAP1 and the C-terminal fragment (cYFP) to WRKY33. Leaves from Nicotiana benthamiana were infiltrated with agrobacteria as indicated.
(F) Y2H assays to assess the interaction between WRKY33 and TTG1. Yeast cells cotransformed with WRKY33/AD and PAP1/BD, TT8/BD, or TTG1/BD were grown on SD/−Trp/−Leu and SD/−Trp/−Leu/−His/−Ade media. The empty vector pGADT7 was used as a negative control.
(G) Yeast three-hybrid (Y3H) assay to explore the influence of WRKY33 on the PAP1–TT8 interaction. The β-galactosidase activity represents PAP1–TT8 binding activities, and the promoter driving WRKY33 expression was suppressed by increasing concentrations of methionine (Met).
(H) Schematic diagram showing the reporter (DFRpro:LUC) and effector (35S:WRKY33, 35S:PAP1, 35S:TT8, and 35S:TTG1) constructs.
(I) Relative firefly LUC-to-REN ratios from transient expression assays. These represent the activity of the DFR promoter in the absence/presence of the MBW (PAP1–TT8–TTG1) complex and the combination of the MBW complex with WRKY33. Error bars indicate the SD of three biological replicates. Different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between groups (P < 0.05; ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test).