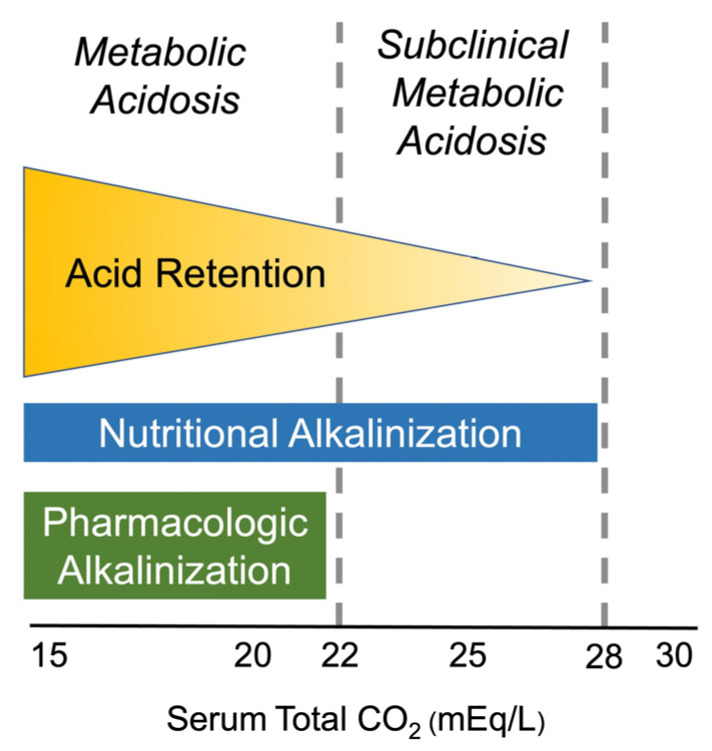
Figure 3.
Conceptual framework of the spectrum of acid retention in chronic kidney disease. Patients with a serum total CO2 < 22 mEq/L have metabolic acidosis and the highest level of acid retention. More mild degrees of acid retention (subclinical metabolic acidosis) are likely present when the serum total CO2 is 22–28 mEq/L. Above a serum total CO2 of 28 mEq/L, the acid–base disorder could either be metabolic alkalosis or respiratory acidosis with metabolic compensation. For the purpose of alkalinization, nutritional therapies can be considered if the serum total CO2 is ≤28 mEq/L so long as the serum potassium concentration is monitored. Generally, the serum potassium should be maintained <5.0 mEq/L. Pharmacological interventions should be reserved for those with total CO2 < 22 mEq/L.