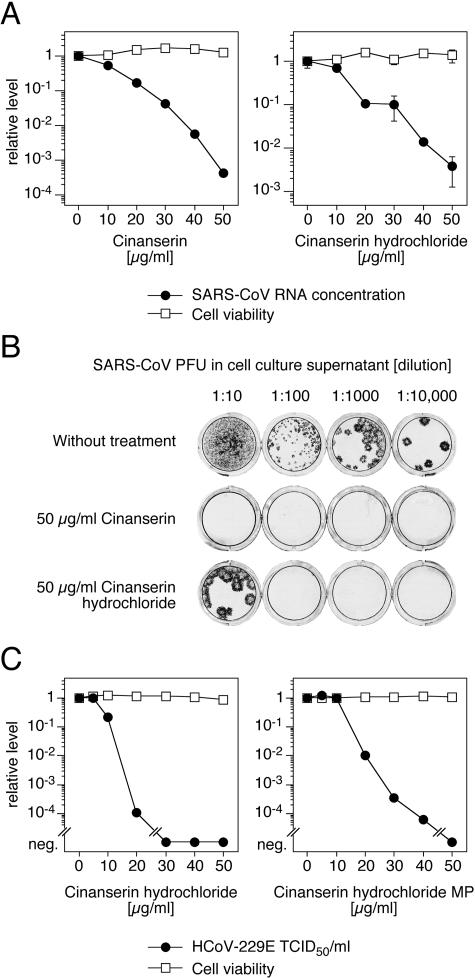
FIG. 5.
Inhibition of SARS-CoV and HCoV-229E replication by cinanserin and cinanserin hydrochloride. (A) Reduction of SARS-CoV RNA concentration in cell culture supernatant. Vero cells were infected with SARS-CoV at an MOI of 0.01, and virus RNA concentration was measured by real-time PCR after 2 days. The influence of the compounds on cell viability was measured by the MTT test. The virus RNA concentration of untreated cells (4 × 107 RNA copies/ml) and the corresponding cell viability value were defined as 1. Means and ranges of duplicate tests are shown. (B) Reduction of SARS-CoV infectious particles in supernatant. Supernatant of infected cells treated with 50 μg/ml compound and of cells that were left untreated were harvested 2 days postinfection, and the numbers of PFU were determined by immunofocus assay. Cell culture wells inoculated with dilutions of the supernatant are shown. (C) Reduction of HCoV-229E titer in cell culture supernatant by cinanserin hydrochloride synthesized in this study (left) or purchased from MP Biomedicals (right). MRC-5 cells were infected with HCoV-229E at an MOI of 0.1, and titers of infectious particles were determined after 2 days. The influence of the compounds on cell viability was measured with CellTitre 96 Aqueous One kit. The virus titer of untreated cells (3 × 105 50% tissue culture infectious dose units/ml) and the corresponding cell viability value were defined as 1. Means of triplicate tests are shown. neg., negative.