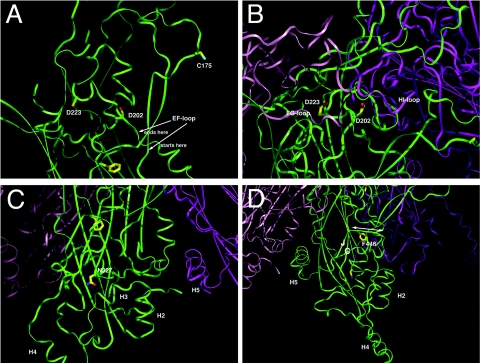
FIG. 6.
In silico analysis of the contribution of residues D202, D223, N327 and F446 to the HPV16 L1 capsomer structure. (A) The D202H mutation may affect the stability of this inner EF loop, which in turn affects the position of the outer EF loop and the C175 position that is implicated in particle assembly. D202H may also influence pentamer conformation by affecting the interface angle between two neighboring molecules in a pentamer, which could also reduce the efficiency of particle assembly in vivo (21). Interestingly, this mutant assembled efficiently in vitro in the absence of chaperones. Thus, chaperones may recognize this mutant in vivo as improperly folded and prevent capsid assembly. (B) Like D202, D223 is also located in the inner EF loop (Fig. 6A). In a pentamer, the surface FG loop from the left neighboring monomer is directly positioned on the top of the D223 and other residues of the inner EF loop. A change of D223G may influence the interactions of the FG loop of the neighboring monomer and affect the pentamer conformation (e.g., the surface loop positioning and the pentamer width), thus reducing the efficiency of particle assembly. However, the C-terminal tail which links capsomers and contains the H16.U4 neutralizing epitope (3) folds such that reactivity with this monoclonal antibody is retained. (C) N327 is located at a turn at the end of the GH loop and at the beginning of the H strand. Its interactions with the surrounding residues help anchoring the GH loop that interacts with H3 (helix 3) and H5 of the neighboring molecule. Both H3 and H5 are important for particle assembly. N327S mutation may lead to a less stabile GH loop, which may affect H3 and H5 interactions and thus assembly. (D) F446 is important for anchoring the stretch of residues of 444 to 447 (indicated by a double arrow) to the core of L1. Residues 444 to 447 are between strands J and H4, both of which are important elements for particle assembly. F446S results in much weaker interactions between the core and residues 444 to 447, which may account for the reduced efficiency of particle assembly.