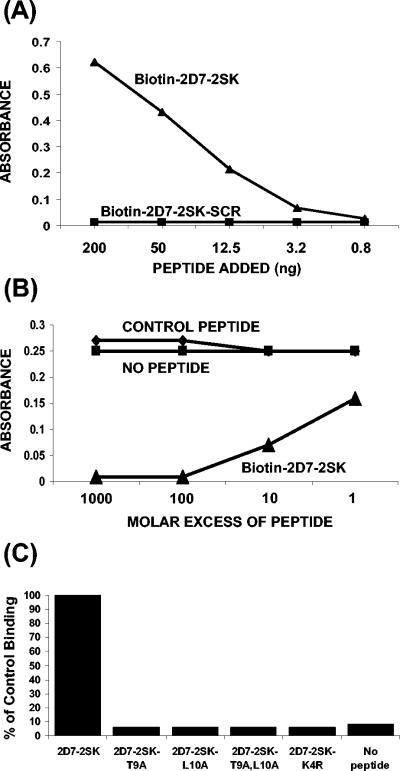
FIG. 3.
Characterization of MAb 2D7 binding to synthetic peptide 2D7-2SK peptide by ELISA. (A) Direct binding of MAb 2D7 to different concentrations of biotinylated-2D7-2SK or to biotinylated-scrambled 2D7-2SK peptide (2D7-2SK-SCR) captured by streptavidin-coated microtiter plates. The bound antibodies were quantified by HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody. (B) Competition of binding of phages displaying peptide 2D7-2SK sequence (p2D7-2SK) to MAb 2D7 by soluble 2D7-2SK synthetic peptide. Microtiter wells, coated with MAb 2D7 at 200 ng/well, were incubated with serially diluted synthetic 2D7-2SK peptide or with a control peptide (CGRAARIGFPGAYTTKNG) for 30 min at room temperature. p2D7-2SK phages were then added to all wells (109 phages/well), followed by addition of HRP-conjugated anti-phage antibodies. (C) Identification of critical residues in the 2D7-2SK peptide sequence required for MAb 2D7 binding. MAb 2D7 (50 ng/100 μl/well) was added to plates coated with either unmodified biotin-2D7-2SK peptide or mutated biotin-2D7-2SK peptide derivatives (Table 1), all captured on streptavidin-coated wells. The bound 2D7 antibodies were quantified by HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody. The absorbance value (0.49) of MAb 2D7 binding to 2D7-2SK peptide (unmodified) is represented as 100% control binding.