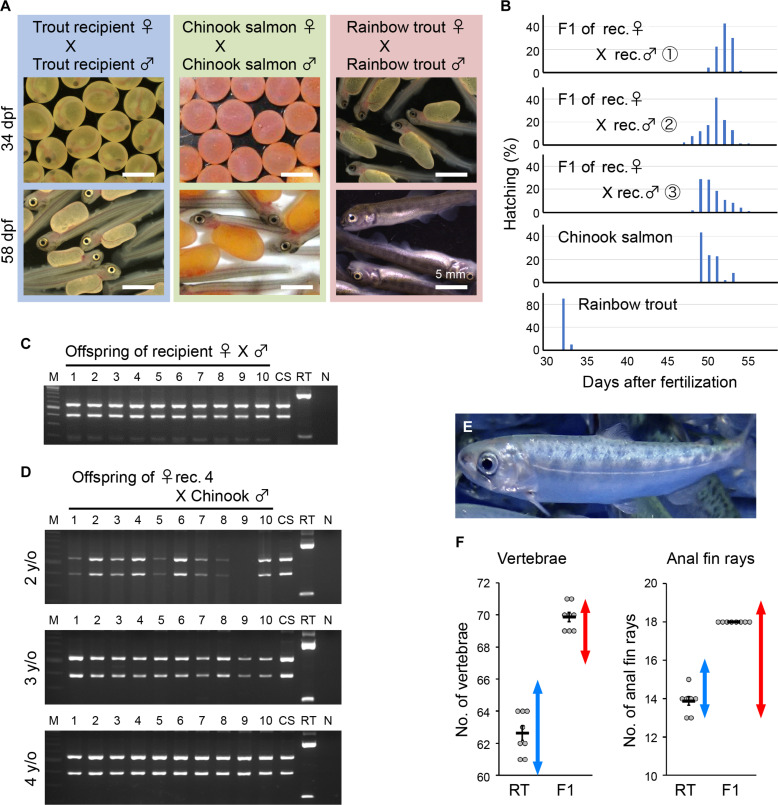
Fig. 3. Production of Chinook salmon offspring by mating dnd-knockout rainbow trout recipients.
(A) Fertilized eggs and hatchlings produced by crosses between male and female trout recipients. The blue, green, and red boxes indicate the offspring of trout recipients, Chinook salmon, and rainbow trout, respectively. The top and bottom panels show offspring at 34 days postfertilization (dpf) and 58 dpf, respectively. (B) Hatching time of the offspring produced by trout recipients. The three randomly selected broods were used for analysis. (C) RFLP analysis of the vasa gene using DNA from the offspring produced by trout recipient parents. Numbers 1 to 10, F1 larvae samples produced by trout recipients; CS, Chinook salmon; RT, rainbow trout. NC indicates the negative control, and M indicates DNA-size marker. (D) RFLP analysis of the vasa gene using DNA from the F1 using eggs from female recipient no. 4, aged 2 to 4 years, and sperm from Chinook salmon. Numbers 1 to 10 represent F1 larvae samples of recipient no. 4. (E) External morphology of the offspring derived from trout recipients. (F) Number of vertebrae and anal fin rays of the offspring produced by trout recipients. RT, values for control rainbow trout; F1, values for the offspring produced by the recipients. Red and blue double-headed arrows indicate the range of respective values for Chinook salmon and rainbow trout from the literature, respectively.