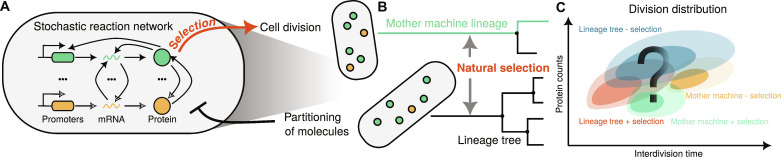
Fig. 1. Quantifying interactions between gene networks and population dynamics with agent-based modeling of clonal populations.
(A) Cartoon of the agent-based model where intracellular reaction network couples to cell division. Intracellular reactions affect cell division rate (red arrow), while partitioning of molecules dilutes cellular expression levels (black repressive arrow). (B) Lineage statistics of agent-based models measure distributions across lineage tree resulting from competition of cells through natural selection. A mother machine lineage (green line) follows a single cell in the lineage tree starting from an ancestral cell and following each daughter cell with equal probability. Mother machine sampling avoids natural selection, i.e., competition of cells for growth (red arrow). (C) Illustration of division distributions for a cell to divide at a given age and protein count for a lineage tree of cells including division-rate selection and natural selection (red), a lineage tree without division-rate selection (blue), and the corresponding mother machine lineages (green and orange).