Figure 3.
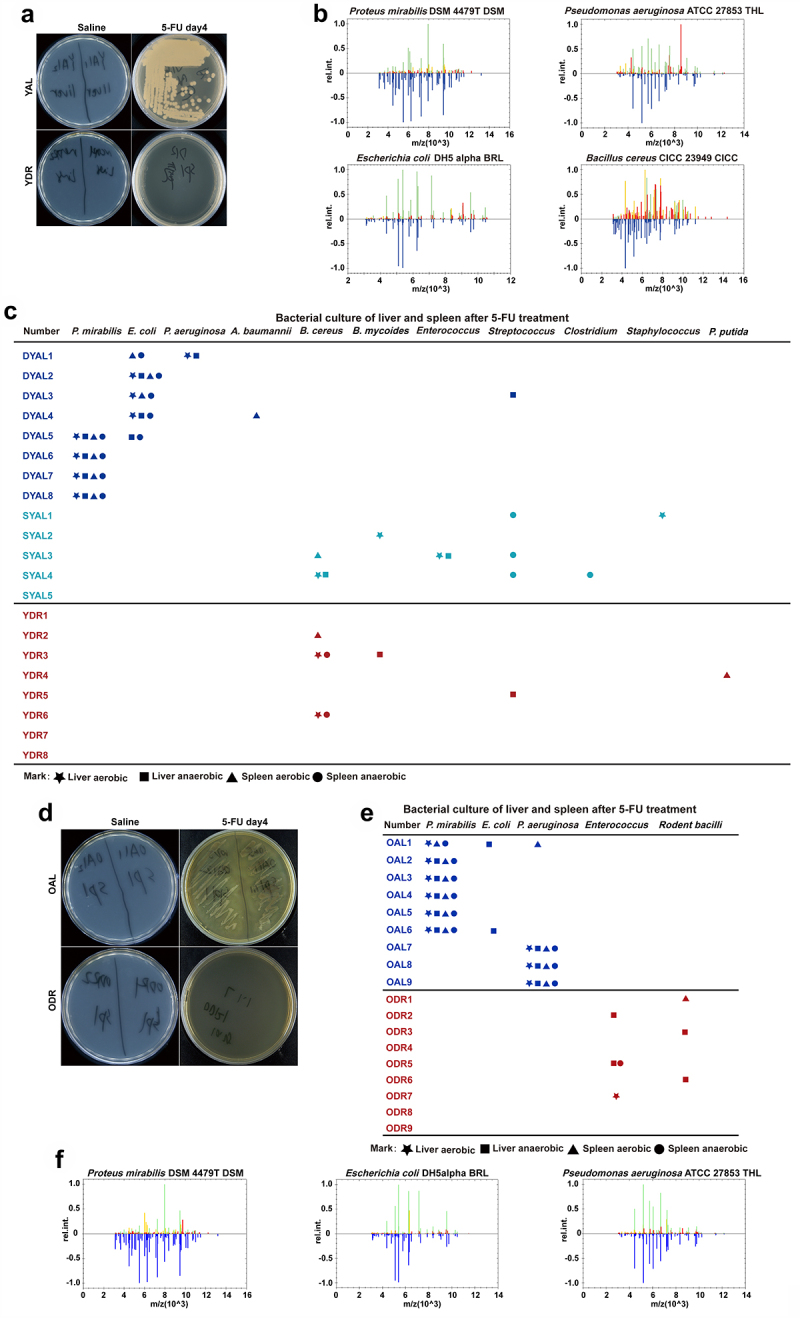
DR inhibits intestinal opportunistic pathogens translocation after 5-FU treatment.
Young mice and old mice (20–24-month-old) were exposed to AL diet or DR for 14 days before intraperitoneal 5-FU injection which was daily performed for 5 days (day -4–day 0), and the diet regimen was continued afterward. For the control group, saline was injected instead of 5-FU. Mice were sacrificed on day 4 after 5-FU treatment and liver and spleen were collected and homogenized for bacterial culture and further analysis.
(A,D) Representative pictures of bacteria culture dishes from indicated groups.
(B,F) The bacterial colonies grown out from the liver and spleen homogenates were identified by mass spectrometer. Above the ordinate 0 scale is the key mass spectral peak data of the target bacteria, which is compared with the known strain spectrum in the database located below the ordinate 0 scale identifying specific bacteria.
(C,E) Bacterial species identified from colonies grown out from individual mouse tissue homogenates. (Data combined from two independent experiments). Mice which met Death or Moribundity Criteria according to Guidelines for Endpoints in Animal Study Proposals after 5-FU were defined as non-survived or dead. Mice which did not meet Death or Moribundity Criteria were defined as survived. DYAL: dead young ad libitum; SYAL: survived young ad libitum.
