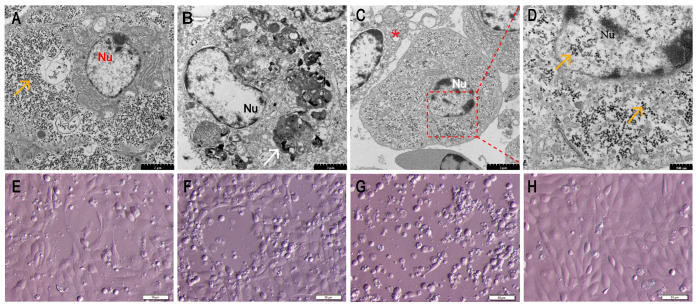
Figure 2.
Identification of the causative pathogen in diseased Chinese tongue soles using transmission electron microscopy and virus isolation. (A) Liver: a large amount of virus particles were presented in the cytoplasm (orange arrow). Nu: nucleus (Bar, 2 μm). (B) Kidney: large, nearly circular inclusions (white arrow) in the cytoplasm near the nucleus (Bar, 2 μm). (C) Spleen: virus particles presented in the cytoplasm and nucleus; necrotic and lysed cells were observed (asterisk) (Bar, 2 μm). (D) Higher magnification of the area bounded by the red rectangle in panel C, showing magnified virus particles (orange arrow) (Bar, 500 nm). (E) FG cells infected with CsPaV and CsPV at passage 1, for 3 days. (F) FG cells infected with CsPaV and CsPV at passage 2, for 5 days. (G) FG cells infected with CsPaV and CsPV at passage 3, for 7 days. Typical CPE was observed (Bar, 50 μm). (H) Normal FG cells.