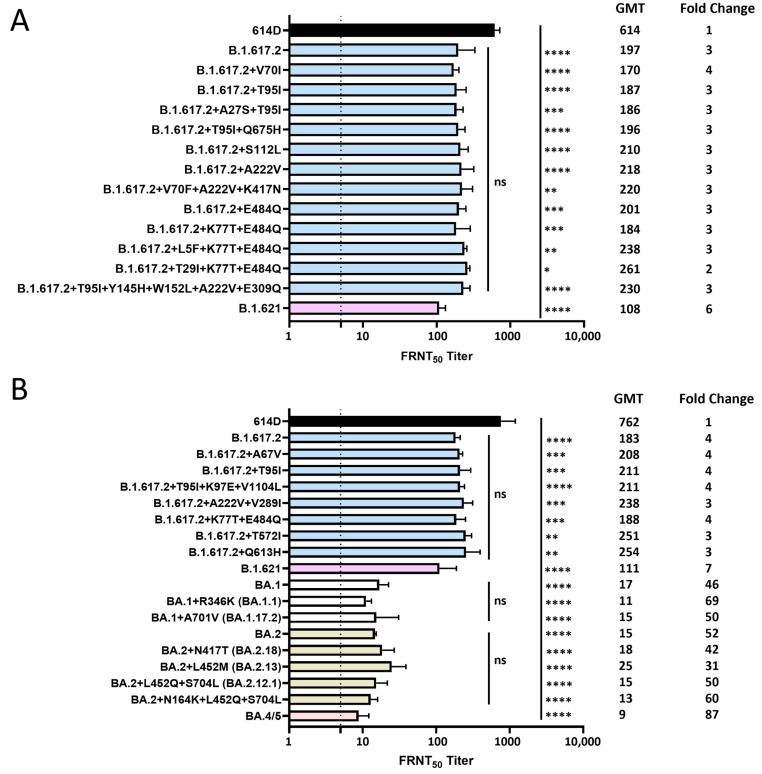
Figure 3.
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Delta, Mu and Omicron variants by pooled monovalent vaccinee sera post the primary series. (A) A Moderna post-primary series pool and a Pfizer post-primary series pool were each generated from 10 volunteers (no prior SARS-CoV-2 infection) who received two doses of the original mRNA monovalent vaccine from either Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech. Each isolated SARS-CoV-2 Delta or Mu variant was analyzed against both sera pools using the focus reduction neutralization test (FRNT), and the average FRNT50 value was used to represent the neutralization titer of that virus against post-primary series sera pool. (B) Post-primary series sera pool with medium range spike-specific antibody titers (1339–3541 BAU/mL) was generated from another five volunteers (no prior SARS-CoV-2 infection) who received two doses of the original mRNA monovalent vaccine (Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech). This post-primary series medium sera pool was analyzed against various SARS-CoV-2 Delta, Mu and Omicron variants with additional spike mutations. Bars represent geometric mean neutralization titer (GMT) with geometric SD from 2–10 independent repeats of virus with the same spike protein sequence. Significance relative to 614D, B.1.617.2, BA.1 or BA.2 was determined by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett correction on log transformed neutralization titers. p values are displayed as * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001 and not significant (ns) p > 0.05. GMT and fold changes compared to 614D are displayed on the side. The dashed line represents the limit of detection at FRNT50 of 5.