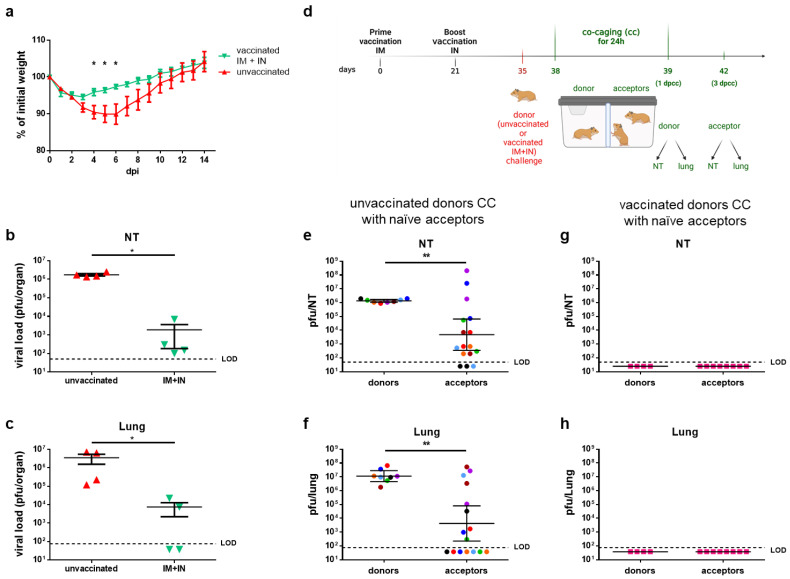
Figure 7.
Heterologous vaccination of golden Syrian hamsters prevents SARS-CoV-2 virus transmission: (a) Body weight changes of unvaccinated hamsters or hamsters vaccinated with heterologous IM + IN injection of VSV–ΔG–spike. The scheme was created with BioRender.com (full license). (b,c) Viral load titers at 3 dpi in the (b) nasal turbinates (NTs) or (c) lungs of unvaccinated hamsters or hamsters following heterologous IM + IN vaccination. n = 4 for each group. (d) Schematic drawing displaying co-caging (“cc”) setting of unvaccinated or vaccinated donors and naïve hamsters following the SARS-CoV-2 infection of donor hamsters. “dpcc” stands for “days post-co-caging”. (e,f) Viral load titers in the (e) NTs or (f) lungs of unvaccinated donors and naïve acceptors following co-caging. (g,h) Viral load titers in the (g) nasal turbinates or (h) lungs of IM + IN-vaccinated donors and naïve acceptors following co-caging. Donors: n = 8; acceptors: n = 16. Each color represents a set of 1 donor and 2 acceptors co-caged. Statistical analysis was performed by a Mann–Whitney nonparametric t-test. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.