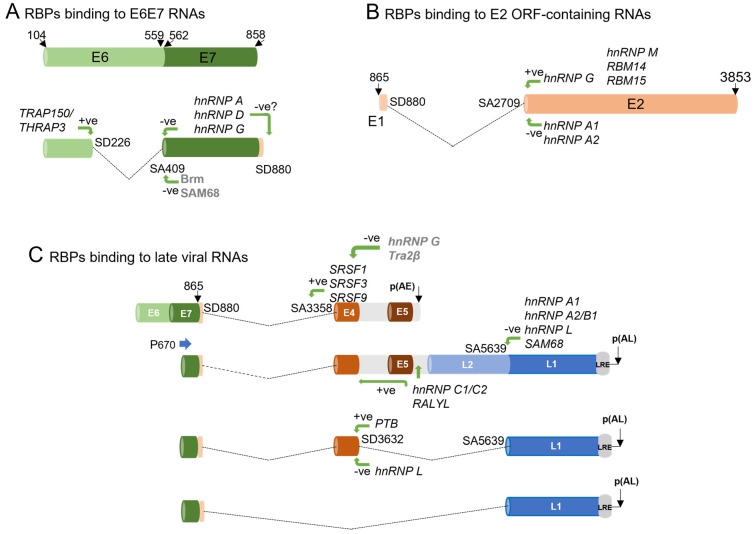
Figure 4.
Diagrams of regions of the HPV16 RNAs shown to interact with RBPs. (A) RBPs interacting with exonic sequence motifs in the E6 and E7 open reading frames. (B) RBPs interacting with exonic sequence motifs in the E2 open reading frame. (C) RBPs interacting with exonic sequence motifs and the early 3′ UTR in viral late RNAs. RBPs not formally shown to bind the RNAs are shown in grey type. The location of the RBP names indicates their approximate binding position on the RNAs. Promoters are indicated with blue horizontal arrows and designated “P” followed by a number. LRE, late regulatory element. p(AE), early polyadenylation site. p(AL), late polyadenylation site. Exons are indicated with horizontal cylinders. Introns are indicated with dotted black lines. Green arrows indicate the positive (+ve) or negative (−ve) effect of various RNA binding proteins on splicing. The approximate binding positions of each of these proteins can be obtained in the review by Kajitani and Schwartz [61].