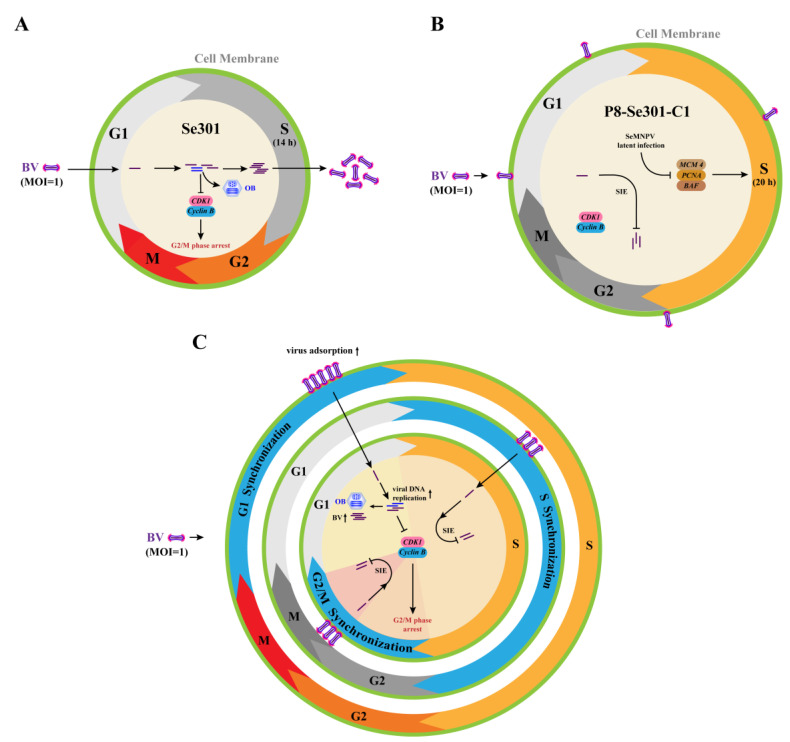
Figure 7.
Schematic of SeMNPV superinfection exclusion alleviation by cell cycle progression regulation in latently infected P8-Se301-C1 cells. (A) Cell cycle progression of Se301 cells infected with SeMNPV. SeMNPV infection of Se301 cells downregulated the expression of Cyclin B and CDK1, induced G2/M phase arrest, and produced progeny BVs and ODVs. (B) Regulation of cell cycle progression in P8-Se301-C1 by SeMNPV superinfection. The expression of DNA replication-related genes MCM 4, PCNA, and BAF was downregulated, and the S phase was prolonged in P8-Se301-C1 cells. SeMNPV superinfection did not change Cyclin B and CDK1 expression or induce G2/M phase arrest, and viral progeny production was inhibited. (C) SeMNPV infection of G1-phase P8-Se301-C1 cells regulated cell cycle progression and partially alleviated SeMNPV superinfection exclusion. SeMNPV superinfection of G1-phase P8-Se301-C1 cells promoted viral adsorption on the cell surface and intracellular viral DNA replication, downregulated Cyclin B and CDK1 expression, induced G2/M phase arrest, and increased the production of BVs and OBs. Synchronization of SeMNPV-infected G1 phase P8-Se301-C1 cells in the G2/M phase further increased progeny virus production. However, SeMNPV infection of S-phase or G2/M-phase P8-Se301-C1 cells did not downregulate Cyclin B and CDK1 expression, and the production of progeny BVs and OBs was deduced.