Figure 7. Allergen-induced stem cell proliferation is independent of type 2 inflammatory pathways and dependent on tuft cells.
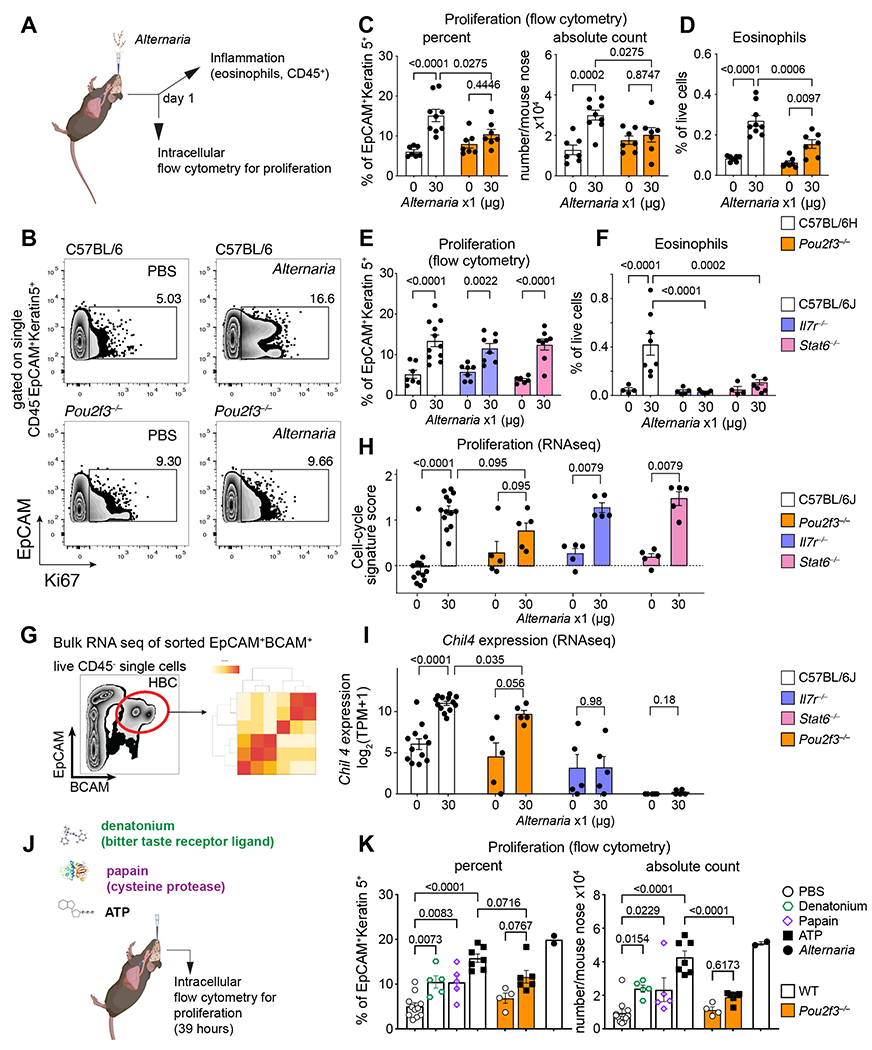
(A-I) Mice of the indicated genotypes were given a single dose of Alternaria intranasally and the nasal mucosa was assessed a day later for stem cell proliferation defined by Ki67 expression of Krt5+ cells (B, C, E) and eosinophil infiltration (D, F) by flow cytometry and for transcriptional reprograming by bulk RNAseq of sorted EpCAM+BCAM+ stem cells (G-I). RNAseq quantification of a validated cell-cycle signature score (Methods) (H), and the IL-13-dependent transcript Chil4 (I). (J-K) WT or Pou2f3−/− mice were given a single intranasal inhalation of denatonium, papain, ATP or Alternaria (color legend, right) and the percent and number of proliferating Krt5+ cells were assessed by intranuclear staining for Ki67 by flow cytometry after 39h. Data are means ± SEM from three independent experiments, each dot is a separate mouse. P-values for FACS quantification in C-F and K are from one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison correction. All other p-values (H-I) are Mann-Whitney U-test.
