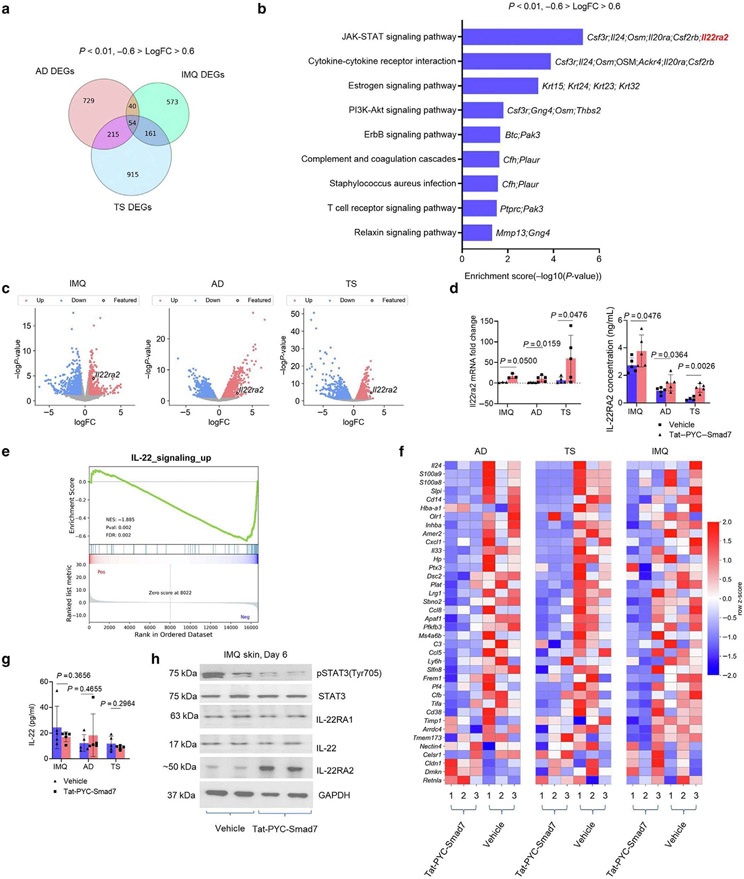
Figure 3. IL-22RA2 is a putative target responsible for PYC-SMAD7-derived IL-22 signaling suppression.
(a) Overlapping *DEGs across transcriptomes of IMQ, AD, and TS skin by Tat-PYC-SMAD7 treatment. (b) Enriched KEGG pathways for overlapping DEGs. (c) Volcano plots for transcriptomes of inflamed skin samples, with Il22ra2 as a common DEG upregulated by Tat-PYC-SMAD7 treatment. (d) mRNA fold change by qPCR and IL22RA2 levels by ELISA using lysates of lesional skin samples. (e) Enrichment plot and (f) heatmap for IL-22 signaling-upregulated genes. (g) IL-22 levels detected by ELISA and (h) western blot for IL-22 signaling markers using protein lysis of lesional skin samples. Samples were qualified using two-tailed unpaired t- or Mann-Whitney U test. Data are representative of three independent experiments with five samples per group. Data represent mean ± SEM. AD, atopic dermatitis; DEG, differentially expressed gene; FC, fold change; IMQ, imiquimod; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; pSTAT3, phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TS, tape stripping.