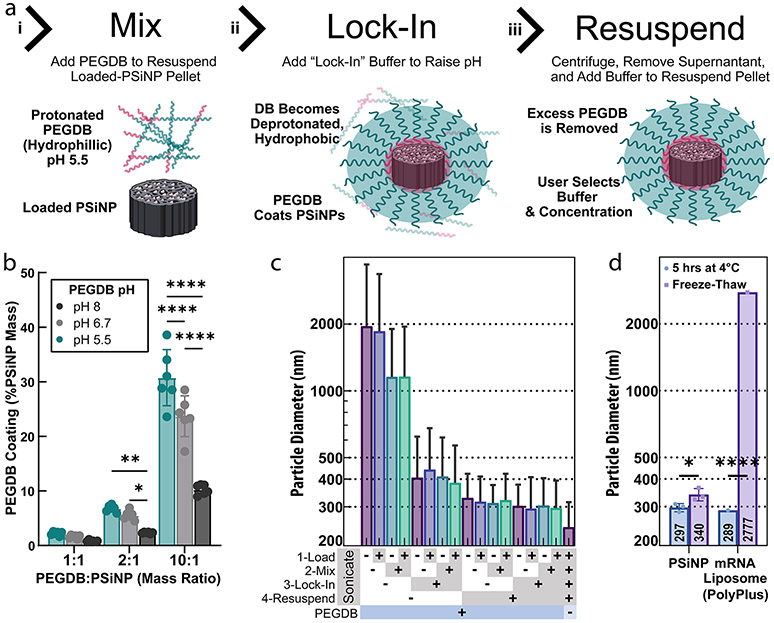
Figure 3.
Optimizing the PEGDB coating of PSiNPs to form nanocomposites. (a) Steps used to form polymer and PSiNP nanocomposites: (i) PEGDB is mixed with PSiNP to “coat” the PSiNP based on electrostatic interactions; (ii) the DB block is deprotonated by raising the solution pH to “lock in” the polymer surface coating around the PSiNP; (iii) the PSiNPs are pelleted by centrifugation, and the excess PEGDB is removed with the supernatant. (b) Relative amount of PEGDB coated onto PSiNPs using different loading buffer pHs. Each data point is an independently prepared replicate, and error bars indicate standard deviation. (c) Z-average diameter of PSiNPs as a function of sonication at each preparation step. Bar colors are for ease of viewing. Each bar is a single sample, and error bars represent standard deviation, calculated from polydispersity index. (d) The stability of PSiNP nanocomposites vs PolyPlus mRNA lipid nanoparticles after incubation at 4 °C for 5 h or flash-freezing and thawing at room temperature. All statistics result from ANOVA with Dunnett’s or Tukey’s multiple comparisons test using GraphPad Prism (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001).