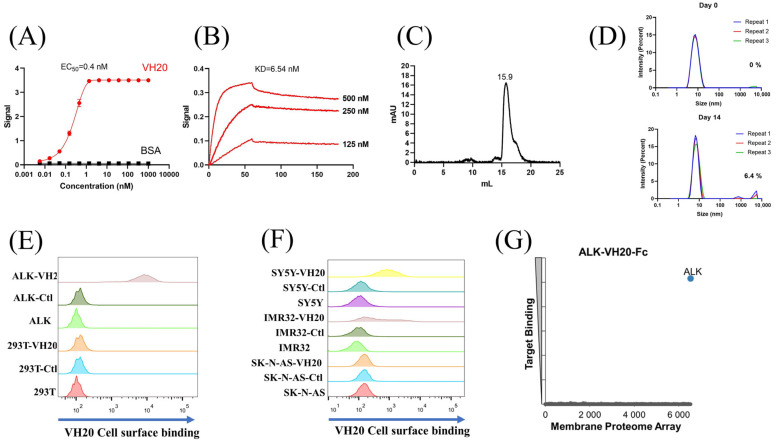
Figure 2.
Characterization of ALK sdAb VH20. (A) ELISA results of VH20 binding to ALK extracellular domain. The BSA was used as a negative control. ELISA samples were tested in triplicate and error bars denote ± SD, n = 3. (B) BLItz result of VH20 binding to ALK-Fc. (C) Aggregation evaluation of VH20 by size exclusion chromatography (SEC). (D) Aggregation evaluation of VH20 by dynamic light scattering (DLS). Antibody was evaluated with a concentration of 2 mg/mL. 6.4% VH20 aggregation was detected after 14 days of incubation at 37 °C. (E) FACS results of VH20 binding to 293T and 293T-ALK cells. VH20 specifically binding to 293T-ALK cells, with none off-target binding to 293T cells. (F) FACS results of VH20 binding to NBL SK-N-AS, IMR-32 and SH-SY5Y cells. VH20 specifically binds to IMR-32, SH-SY5Y cells with no binding to SK-N-AS cells. (G) Membrane Proteome Array (MPA) result of VH20-Fc (20 μg/mL) against different human membrane proteins (>6000) and no non-specific binding was detected.