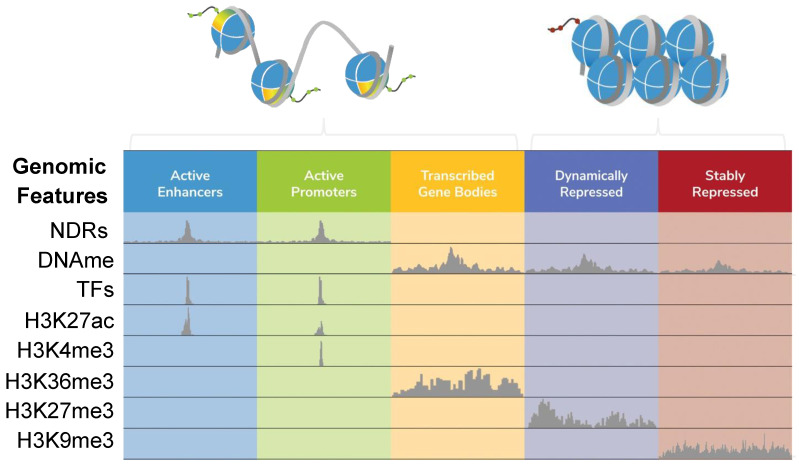
Figure 1.
Local features that define ‘open’ and ‘closed’ chromatin. Chromatin states (e.g., active transcriptional enhancers or repressed heterochromatin) can be functionally defined by integrating a range of data elements, including nucleosome-depleted regions (NDRs; mapped by one of the methods discussed in this review), DNA methylation (DNAme (primarily 5-methylcytosine); mapped by bisulfite sequencing or EM-seq [18,19]), transcription factors (TFs) and histone post-translational modifications (PTMs, such as H3K27ac, H3K4me3, H3K36me3, H3K27me3, and H3K9me3) mapped by ChIP-seq, or newer approaches like CUT&RUN or CUT&Tag [20,21]. The figure was adapted from [22]. The extended stretch of nucleosome-free DNA at an active promoter represents an NDR.