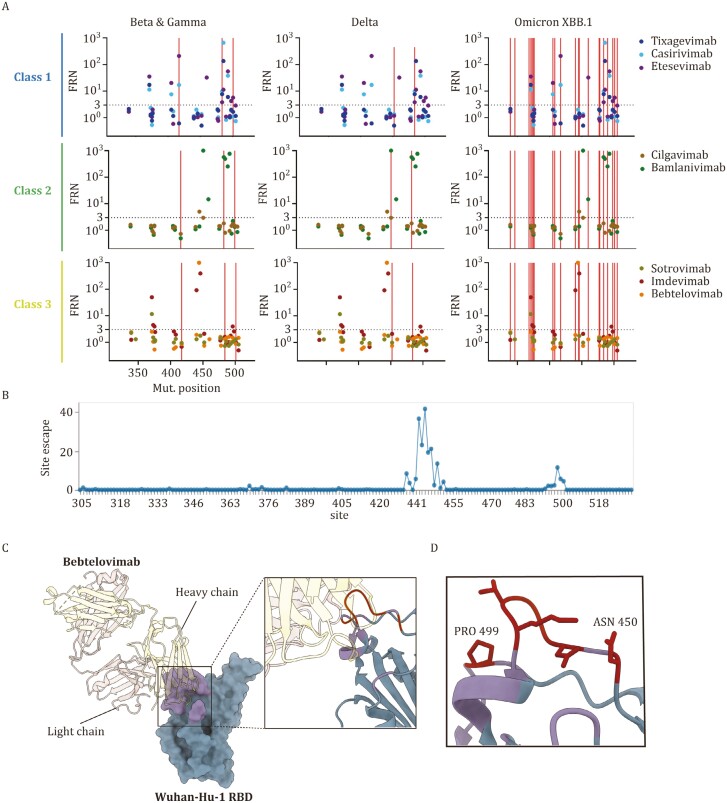
Figure 2.
Epitope mutations drive resistance to antibody neutralization. (A) Geometric mean fold reduction in neutralization (mFRN) data for each class of monoclonal antibody (mAb). The mFRN values (y-axis) was determined using the wildtype pseudoviruses containing only one single mutation in the RBD of S protein (positions 305–534, x-axis) (Shang et al., 2020), with the wildtype pseudovirus as the reference control. Each dot represents the mFRN value of one mutation-mAb pair (mutation sites refer to Fig. 1A). The colors of dots represent the corresponding testing mAbs. Horizonal dashed line shows the mFRN = 3 threshold. Mutation sites of representative VOCs Beta, Gamma, Delta and Omicron XBB.1 (see Fig. 1A) are indicated by vertical red lines. The full dataset of mFRN values for each mAb in the presence of single RBD mutations are summarized in the Supplementary Data File 3. (B) Total escape scores of bebtelovimab (LY-CoV1404) determined by a full spike deep mutational scanning system at each site in the BA.1 RBD. A detailed explanation of escape score could be found in the reference (Yu et al., 2022). An interactive data set is available at Github. (C) X-ray crystal structure of the bebtelovimab Fab bound to the S protein RBD (PDB 7MMO). The rectangular region indicates the Wuhan-Hu-1 RBD epitope recognized by bebtelovimab and is showed as ribbons in the zoomed view. The key escape sites, such as N450 and P499, correspond to the region (site 444-450 and 499) with escape score > 10 (see Fig. 2B). (D) Key escape sites in (C) are showed as atoms.