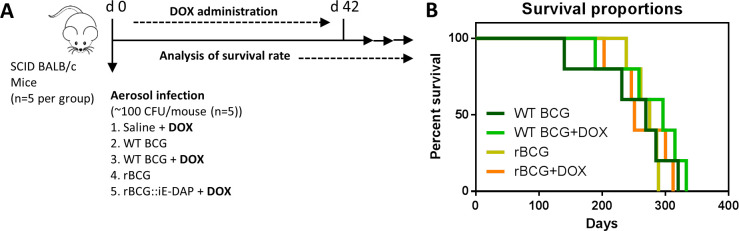
Figure 3. Analysis of rBCG::iE-DAP strain attenuation.
(A) Schematic representation of SCID mice aerosol infection with WT BCG and rBCG::iE-DAP for analysis of strain attenuation. rBCG::iE-DAP activation in vivo was performed by administration of Dox at 1 mg/kg/day. SCID mice (n=5 per group) were aerosol infected with ~2.5 log10 CFU of WT BCG or rBCG::iE-DAP, a WT BCG+Dox group was included as a control. (B) Percent survival of SCID mice following low-dose challenge with WT BCG and rBCG compared to WT BCG+Dox or rBCG+Dox groups. Five mice per group (n=5) were used for the in vivo experiments. student t-test was used for statistical analysis.